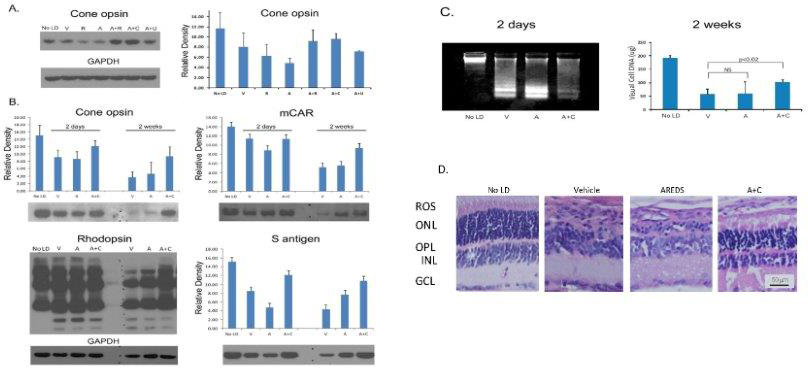
Figure 4. Rats reared in low cyclic light and fed antioxidants for 1 week prior to photooxidative stress. Western analysis of cone opsin
2 days after intense light treatment (
A). Cone opsin, rhodopsin, mCAR and S-antigen levels 2 days or 2 weeks after intense light exposure (
B). Vehicle (V), rosemary (R), AREDS (A), AREDS + rosemary (A+R), AREDS + carnosic acid (A+C), or AREDS + ursolic acid (A+U)
treated rats, concentrations as shown in
Table 1. Density determined by Image J analysis for 3 separate gels (20 µg protein/lane) from n=4-6 rats; error bars ± SD. Retinal
DNA damage and DNA levels determined 2 days or 2 weeks (respectively) after photooxidative damage; No LD; n=8 retinas from
8 different rats (
C). Retinal histology for V, A, or A+C fed rats 2 weeks after intense light treatment (
D).
A: Cone opsin staining was greater for rats fed A+R or A+C, than those fed R, A, or A+U (n=6).
B: Two weeks after retinal light damage cone opsin and mCAR levels were lower than after 2 days, but the relative staining
for A+C (15.8 mg /kg) fed rats remained higher than for those fed A alone. Two weeks after light damage overall rhodopsin
staining was less than in rats after 2 days for those given V or A. Lower molecular weight degradation products were present
after both 2 days and 2 weeks, but higher levels of rhodopsin (and its polymeric forms) were present in animals fed A+C.
C: Two days after light exposure staining for low molecular weight apoptotic DNA fragments was greater for rats treated with
V or A than seen for rats treated with A+C. As determined by ethidium staining of a gel run for only 5 min DNA loading was
the same in all samples (Appendix 3). Two weeks after intense light a significantly higher level of visual cell DNA was found
in rats fed A+C than seen for V treatment (p<0.02).
D: Histology of fellow eyes revealed considerable damage in V and A treated rats (1 to 3 rows of nuclei in the ONL), and retention
of 7-8 rows of nuclei in the ONL of rats fed A+C (bar =50 µm).
 Figure 4 of
Wong, Mol Vis 2017; 23:718-739.
Figure 4 of
Wong, Mol Vis 2017; 23:718-739.  Figure 4 of
Wong, Mol Vis 2017; 23:718-739.
Figure 4 of
Wong, Mol Vis 2017; 23:718-739.