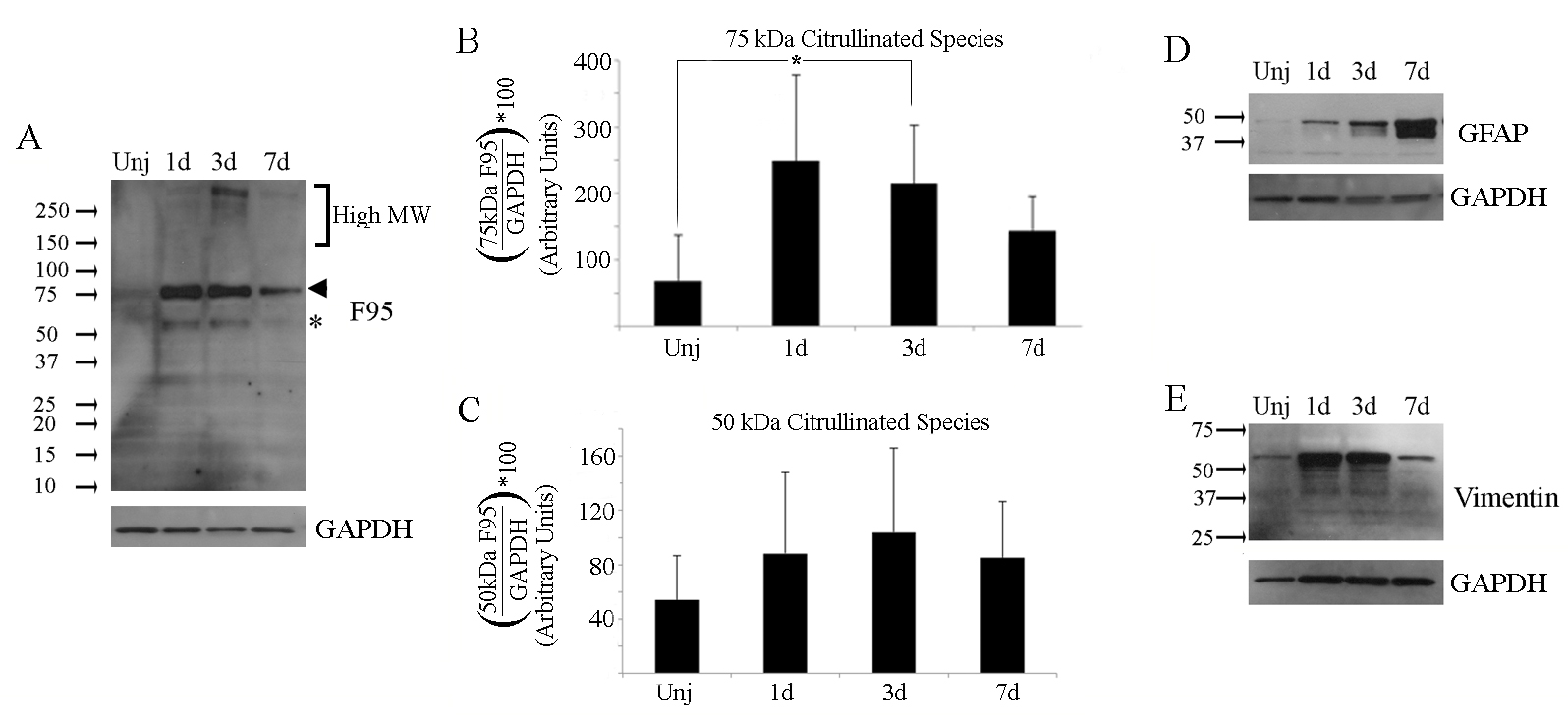
Figure 2. Detection of insoluble citrullinated proteins after ocular alkali injury. Western blot analysis of insoluble proteins from
retinochoroidal tissues from uninjured and injured mouse eyes were carried out as described in
Figure 1. Gel blots were probed sequentially for citrullinated proteins (F95), GFAP and vimentin. Corresponding GAPDH loading controls
are located beneath each blot.
A: Citrullinated proteins were detected in all insoluble fractions with major bands detected at 75 kDa (arrowhead) and at 50
kDa (asterisk), with minor bands over the high molecular weight range between 150 kDa and 250 kDa (bracket).
B,
C: Bar graphs representing quantification of the 75 and 50 kDa citrullinated species, respectively.
D: GFAP isoforms were detectable at all time points below 37 kDa and 50 kDa.
E: A 55 kDa vimentin isoform was detectable at all time points. Each sample contained tissue extracts pooled from 3 retinas
from which protein that was not solubilized in low-salt buffer was extracted as described in Methods. Experiments were repeated
three times (
n=3). Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). P values less than 0.05 (asterisk) were considered significant
as determined by
t test.
 Figure 2 of
Wizeman, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1137-1155.
Figure 2 of
Wizeman, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1137-1155.  Figure 2 of
Wizeman, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1137-1155.
Figure 2 of
Wizeman, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1137-1155.