Figure 4. Effect of FAM18B knockdown on human retinal microvascular endothelial cell migration. The migration of human retinal microvascular endothelial
cells (HRMECs) in various treatment groups are expressed as percent change of HRMECs transfected with scrambled control siRNA
and treated with medium alone. A: Migration of HRMECs transfected with scrambled control siRNA or FAM18B siRNA in the presence or absence of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC). FAM18B knockdown significantly increases the basal migration of HRMECs. B: Migration of HRMECs transfected with scrambled control siRNA or FAM18B siRNA treated with or without vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). C: Migration of HRMECs transfected with scrambled control siRNA or FAM18B siRNA treated with or without high glucose. PDTC is a specific nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) inhibitor. VEGF and glucose
significantly increase the migration of control cells. The VEGF and glucose-induced migration is further potentiated in FAM18B siRNA-transfected cells. The data are represented as mean±standard deviation (SD) * p-value <0.05 compared to control cells
treated with media alone. † p value <0.05 compared to FAM18B siRNA-transfected cells.
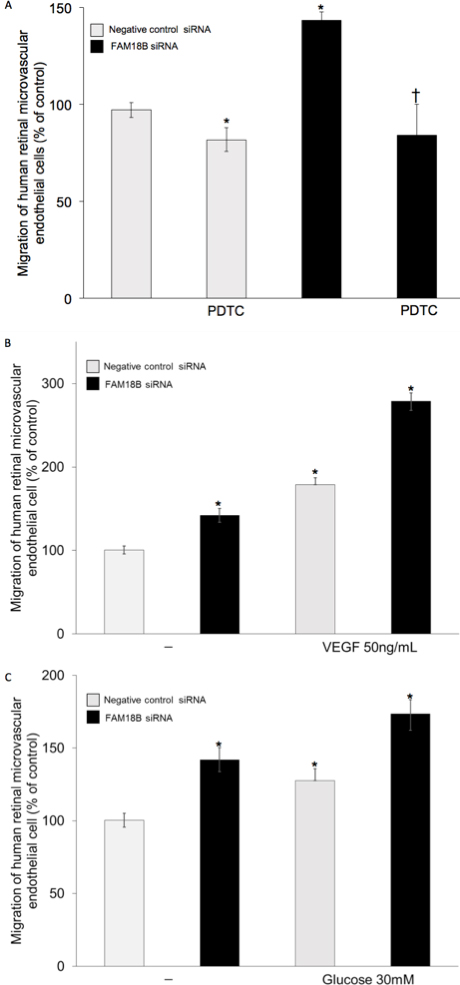
 Figure 4 of
Wang, Mol Vis 2014; 20:1146-1159.
Figure 4 of
Wang, Mol Vis 2014; 20:1146-1159.  Figure 4 of
Wang, Mol Vis 2014; 20:1146-1159.
Figure 4 of
Wang, Mol Vis 2014; 20:1146-1159. 