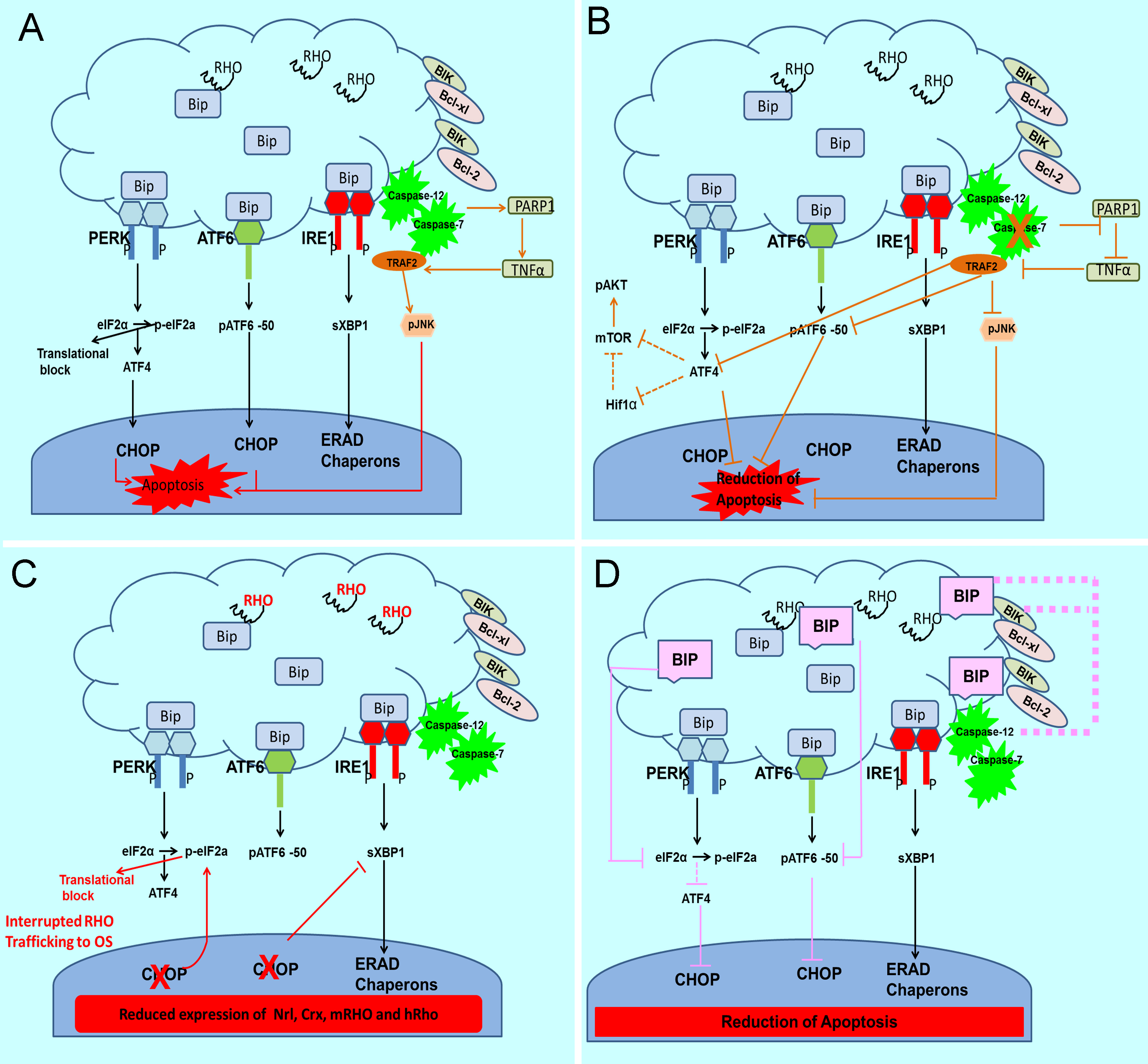
Figure 1. The unfolded protein response (UPR) is activated in the autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (adRP) retina and proposed
to be a target for modulating the rate of retinal degeneration.
A: Activation of the UPR occurs in the adRP retina [
65,
67,
72]. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress mediators pancreatic ER kinase (PKR)-like ER kinase (PERK), inositol-requiring protein
1 (IRE1), and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) are activated during ER stress. During normal cellular homeostasis,
the immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein (GRP78/BiP) is tightly bound to all three mediators. In the presence of unfolded
proteins, BiP dissociates from the three mediators to assist in appropriate protein folding leading to activation of the PERK,
ATF6 and IRE1 UPR arms. In addition to endoRNase activity, phosphorylated (p) IRE1 can activate the c-Jun N-terminal kinase
(JNK) that is known to induce apoptosis through tumor-necrosis factor (TNF)-receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) and ASK1
(apoptotic signaling kinase 1) [
25,
91]. In mammals, recruitment of TRAF2 by pIRE1 allows it to signal to c-Jun N-terminal kinase. The IRE1–TRAF2 complex has also
been linked to caspase-12 activation and cell death. Caspase-12 is activated [
92] in addition to the calpains and Ca2+-induced activation by caspase-7 that translocates to the ER during ER stress [
93]. Activation of the UPR in the adRP retina is accompanied by upregulation of the TNFα and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1
(PARP1) proteins [
72,
94].
B: CASP7-ablation in the T17M
RHO retina leads to a decreased rate of retinal degeneration in T17M
RHO mice. We found that ablation of CASP-7 in adRP retinas leads to a therapeutic effect detected by electroretinogram (ERG),
optical coherence tomography (OCT), and histology [
72]. The CASP-7 ablation also modulates UPR signaling. Reduction in BiP, ATF6, ATF4, Bim, Bik, Edem2, and eIF2α was detected,
suggesting that UPR signaling is modulated in these mice. The second pathway modified by ablation of CASP-7 is the mammalian
target of rapamycin/protein kinase B (mTOR/AKT) signaling resulting in downregulation of mTOR and increase of pAKT in T17M
RHO CASP-7 mice. Finally, ablation of CASP-7 led to the diminishing of TRAF2-JNK-induced apoptosis. This reduction may have occurred
through the inhibition of PARP1, which is known to be cleaved by CASP-7. The PARP1 inhibition in turn perhaps led to the downregulation
of TNFα resulting in a decrease in TRAF2-pJNK signaling through PARP1-TNFα-tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated
death domain-receptor-interacting serine/threonine protein kinase 1-(TADD-RIPK1)-ASK1-pc-JUN.
C: Ablation of proapoptotic CHOP accelerated retinal degeneration in adRP mice through reprogramming the UPR. Detrimental effects
from the ablation of proapoptotic CHOP were detected with ERG, OCT, and histology [
71]. We found that ablation of CHOP leads to a greater than eightfold increase in peIF2α and 30% reduction in spliced Xbp1.
These changes were accompanied by accumulation of the RHO protein in the cytoplasm of the photoreceptors [
71]. Therefore, we concluded that ablation of CHOP in adRP photoreceptors may be linked to global inhibition of protein translation.
An observed increase in the histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) levels supported this hypothesis.
D: Overexpression of GRP78/BiP in the adRP retina slowed the rate of retinal degeneration. Adeno-associated viral (AAV) delivery
of GRPP78/BiP to adRP photoreceptors led to an increase in ERG amplitudes during 3 months [
65]. Overexpression of BiP reprograms the UPR by reducing peIF2α (the PERK pathway) and pATF6-50 (the ATF6 pathway) leading
to a decrease in proapoptotic CHOP. In addition, BiP binds to caspase-12, thus further preventing from induction of apoptosis.
Finally, BiP forms a complex with Bcl-interacting killer (BIK) preventing the translocation of Bcl-2-associated X protein
(BAX) and Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer (BAK) to the mitochondria. We thus concluded that preservation of photoreceptor
function resulting from elevated levels of BiP is due to suppression of apoptosis rather than to promotion of rhodopsin folding.
 Figure 1 of
Gorbatyuk, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1985-1998.
Figure 1 of
Gorbatyuk, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1985-1998.  Figure 1 of
Gorbatyuk, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1985-1998.
Figure 1 of
Gorbatyuk, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1985-1998.