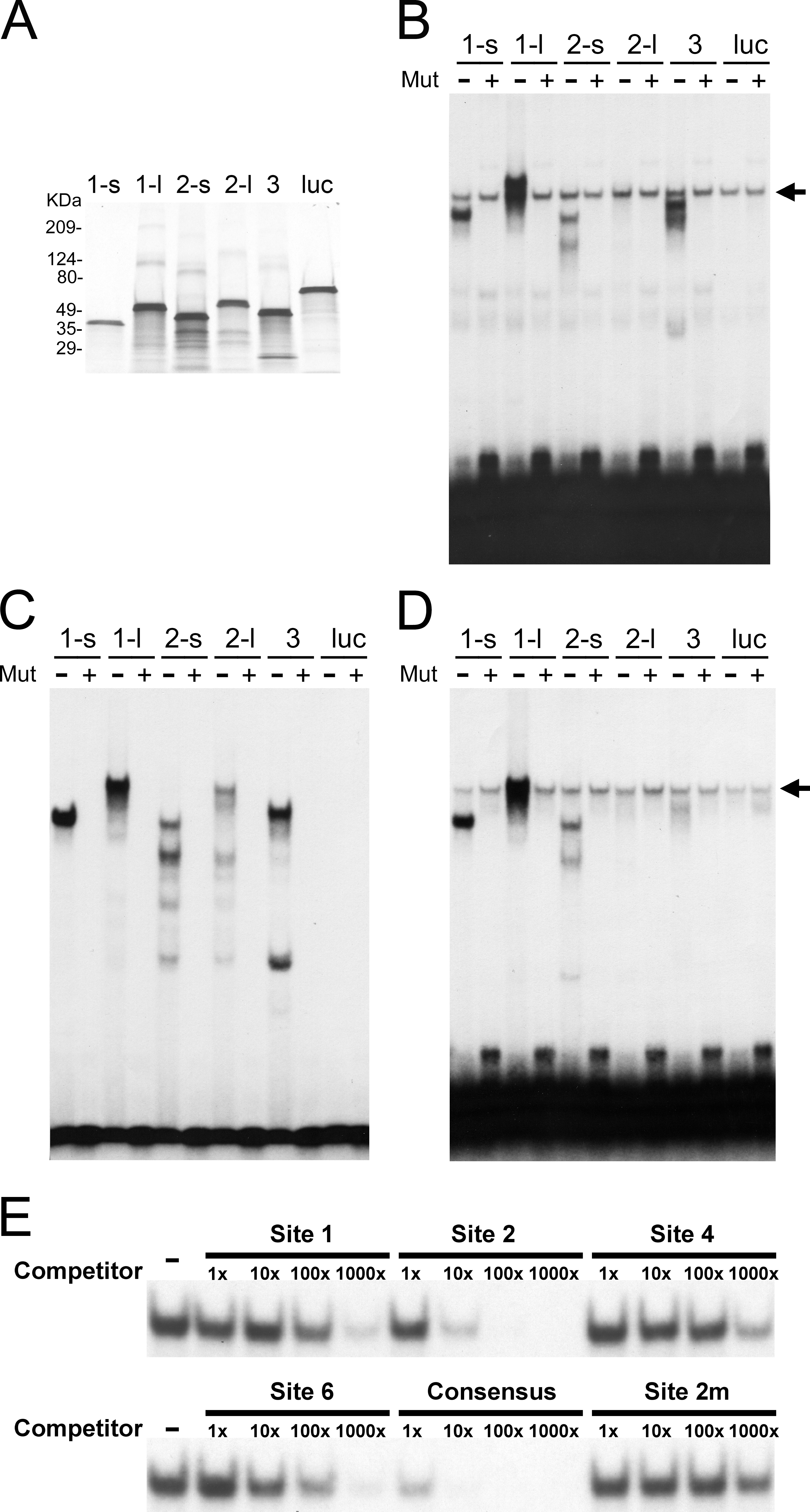
Figure 5. POU4 proteins bind to the predicted sites in a sequence-specific manner.
A: This panel shows POU4 proteins produced by in vitro transcription and translation. The efficiency of protein synthesis was
tested by labeling proteins with
35S-methionine during translation, followed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) fractionation
and autoradiography. Proteins were POU4F1-s (labeled as 1-s), POU4F1-l (1-l), POU4F2-s (2-s), POU4F2-l (2-l), POU4F3 (3),
and luciferase (luc).
B: Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) was performed with probes containing Site 1. The sequence of Probe 1, which
is 24 bp annealed oligonucleotides containing Site 1 in the middle, is shown in
Figure 4. Mutated Probe 1 contains a mutation (TTAA to GGCC) in the core binding sequence of Site 1. Either
32P-labeled wild-type (labeled as Mut -) or mutated (Mut +) Probe 1 was incubated with 3 μl of each in vitro translated protein.
A non-specific band seen in all lanes is indicated by arrow. Proteins were same as in A.
C: This panel shows EMSA with probes containing Site 2. The experimental design and result presentation are the same as in
B, except that Probe 2 containing Site 2 was used, and a non-specific band was not observed.
D: This panel shows EMSA with probes containing Site 6. The experimental design and result presentation are the same as in
B, except that Probe 6 containing Site 6 was used.
E: EMSA was also performed for cold oligomer competition.
32P-labeled Probe 2 was mixed with 1x, 10x, 100x, and 1000×(fold) molar excess of unlabeled competitors, and then incubated
with POU4F1-s protein. Competitors used were oligonucleotides containing Sites 1, 2, 4, 6, mutated 2 (2m), and the reported
POU4F1 consensus site. Binding with no competitor (labeled as Competitor -) is included as control.
 Figure 5 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1371-1386.
Figure 5 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1371-1386.  Figure 5 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1371-1386.
Figure 5 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1371-1386.