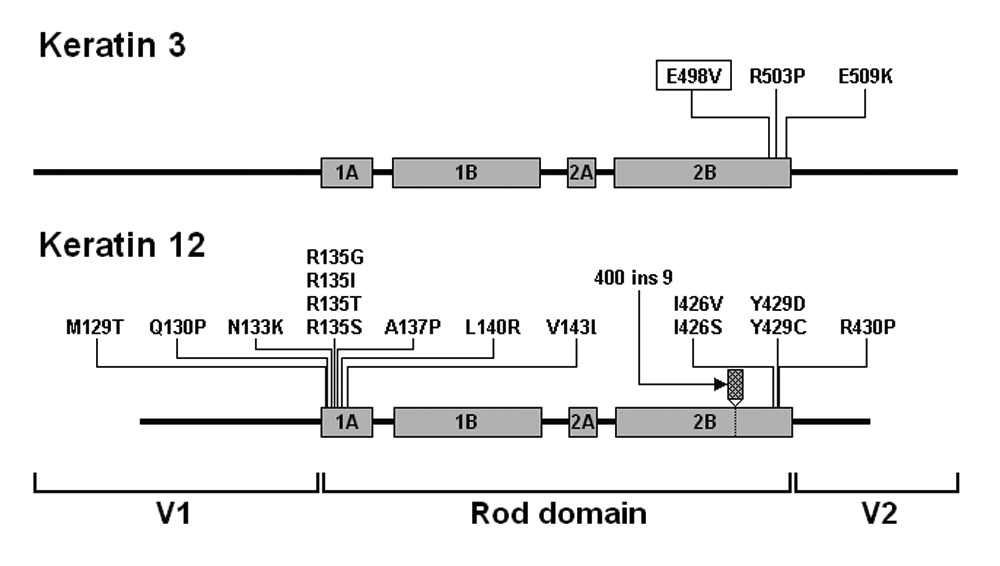
Figure 4. Schematic drawing of K3 and K12
structure with assigned positions of the published mutations. Keratins
are composed of three main parts, the central α-helical rod domain,
which is divided into four subdomains (1A, 1B, 2A, and 2B), and the two
non-helical variable domains (V1 and V2) at each end [
3]. All three mutations
within
KRT3 localize exclusively in the boundary motif of the
2B subdomain. Among the mutations in
KRT12, 11 were found in
the 1A subdomain and six in the 2B subdomain (see also
Table 2).
![]() Figure 4 of Szaflik,
Mol Vis 2008; 14:1713-1718.
Figure 4 of Szaflik,
Mol Vis 2008; 14:1713-1718.