![]() Figure 9 of
McMahon, Mol Vis 2007;
13:258-272.
Figure 9 of
McMahon, Mol Vis 2007;
13:258-272.
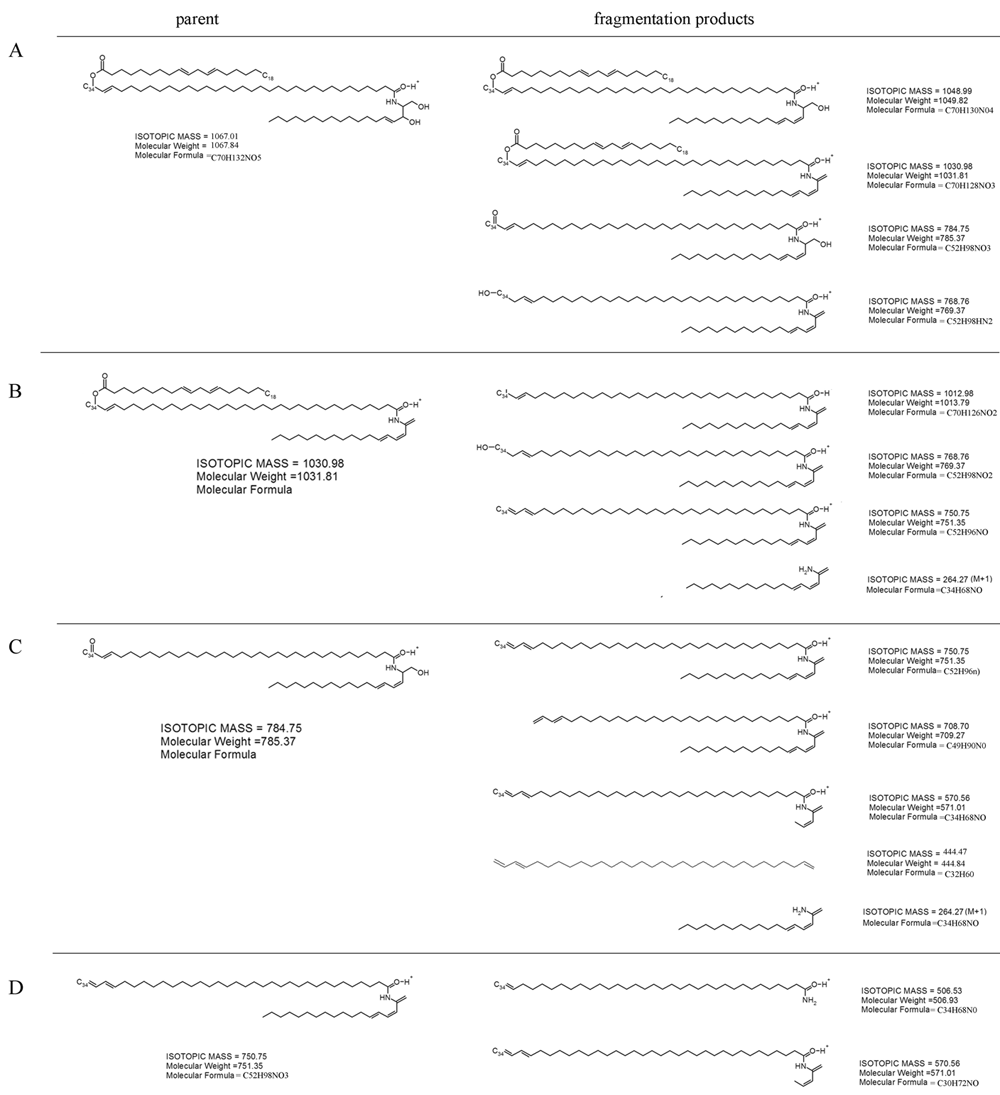
Figure 9. Fragmentation analysis of wild-type epidermal ceramide
The MS positive mode 1066.4 m/z peak (see Figure 7A) was fragmented by collision-induced dissociation and resulted in generation of 1048.1, 1030.6, 744.2, and 769.0 m/z daughter ions. Chemical structures for compounds of these molecular masses are provided in panel A: Further fragmentation of the 1030 m/z ion produced 1012.9, 768.6, 750.7, and 263.9 m/z signals (deduced compound formulas are shown in panel B). Transformation of the 768.6 m/z ion yielded 750.5 + 708.7 + 570.3 + 444.3 + 263.9 m/z ions (C), and fragmentation of the 750.5 m/z ion produced 571.1 and 506.2 m/z ions (D). The observed daughter ions are consistent with fragment compounds expected from C34:1-EOS ceramide which contains sphingosine linked to an ω-hydroxy C34 monounsaturated fatty acid that is esterified with linoleic acid.