![]() Figure 5 of
Steele, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1200-1210.
Figure 5 of
Steele, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1200-1210.
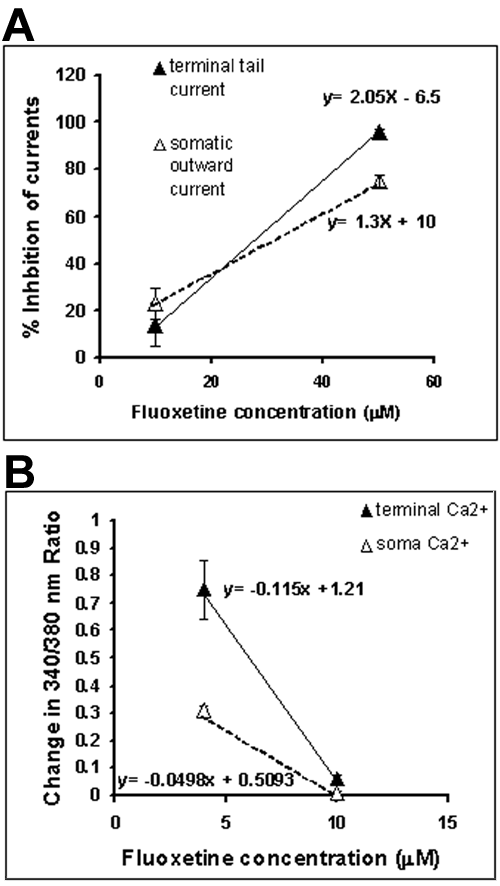
Figure 5. Effects of fluoxetine on terminal currents and intracellular calcium changes are more steeply dose-dependent than those on somatic currents and somatic intracellular calcium changes
The effects of fluoxetine on terminal ICl(Ca) currents and intracellular calcium changes are more steeply dose-dependent than those on somatic IK(Ca) currents and somatic intracellular calcium changes following depolarization. A: Mean percentage current inhibitions for terminal ICl(Ca) (solid triangles connected by solid line) and somatic IK(Ca) (open triangles connected by dashed line) are plotted against fluoxetine concentrations used (10 μM and 50 μM). The data were fitted with linear functions as indicated to estimate the slope as an indication of dose dependency of inhibition of the currents in the two compartments. Note that the slope of the fitted line is greater for terminal ICl(Ca). B: Mean depolarization-induced changes in intracellular calcium levels of rod terminals (solid triangles connected by solid line) and somata (open triangles connected by dashed line), monitored with fura-2 as changes in 340/380 nm ratios, are plotted against fluoxetine concentrations used (4 μM and 10 μM). The data were fitted with linear functions as indicated to estimate the slope as an indication of dose dependency of calcium changes in the two compartments. Note that the slope of the fitted line is greater for terminal calcium changes than somatic calcium changes.