![]() Figure 4 of
Steele, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1200-1210.
Figure 4 of
Steele, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1200-1210.
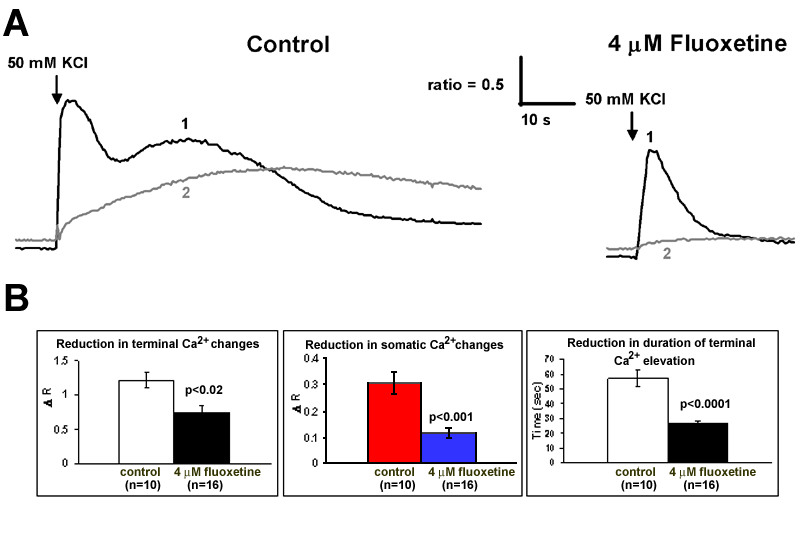
Figure 4. Fluoxetine reduces duration of elevated intracellular calcium levels in salamander rod photoreceptors following depolarization
Fluoxetine (4 μM) in the bath reduces the duration of the normal sustained elevation of intracellular calcium levels in both somatic and terminal compartments of salamander rod photoreceptors following brief depolarization with 50 mM K+. A: Representative trace of changes in intracellular calcium levels within the terminal (1) and somatic (2) compartments are plotted as changes in 340/380 nm ratios over time following a brief depolarizing puff (indicated by the arrow) of 50 mM K+ (pipette concentration) in control bath solution for one cell and bath solution containing 10 μM fluoxetine for another cell. B: Statistical comparison of changes in calcium, shown as changes in the 340/380 nm fluorescence ratio over time (in seconds), of somatic and terminal compartments of cells stimulated in the presence of control bath solution (n=10) or bath solution containing 10 μM fluoxetine (n=16). Note that while 4 μM fluoxetine had a smaller effect than 10 μM on the rise of intracellular calcium in both the somatic and terminal compartments following depolarization, it had a larger and more significant effect on the duration of sustained calcium elevation in the terminal compartment.