![]() Figure 2 of
Bright, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1141-1150.
Figure 2 of
Bright, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1141-1150.
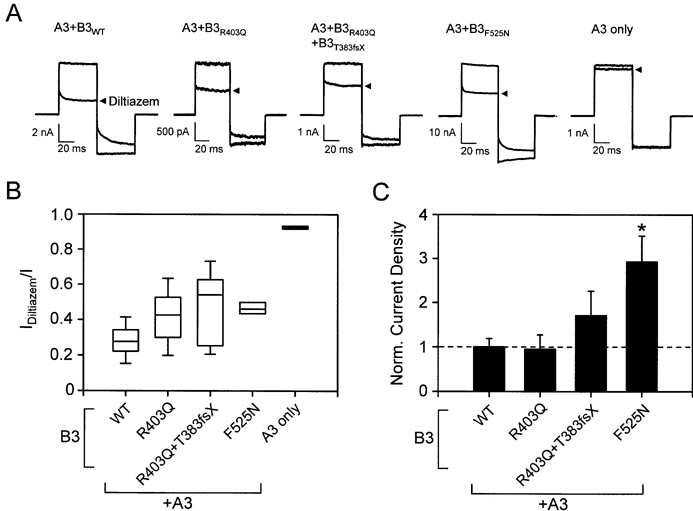
Figure 2. CNGB3 mutant subunits form heteromeric channels
A: Representative current traces are shown for channel activation by saturating (1 mM) cGMP in the presence (arrowhead) or absence of 25 μM L-cis-diltiazem. Traces were elicited by voltage steps from a holding potential of 0 mV to +80 mV, then to -80 mV and 0 mV. Leak currents in the absence of cyclic nucleotide were subtracted for all recordings. B: Box plots are shown for the ratio of current in the presence and absence of 25 μM L-cis-diltiazem, at +80 mV and 1 mM cGMP, for wild-type heteromeric (N=15) and homomeric (N=4) channels and mutant heteromeric channels (N=6 to 16). The line within the box represents the median; the box indicates the 25th and 75th percentiles, while the whiskers show the 5th and 95th percentiles. Each mutant group was significantly different from both the heteromeric and homomeric wild-type groups with an alpha level of 0.05. No significant differences were found between the mutant groups. C: A bar graph is shown of current density normalized to the mean wild type current density for the relevant set of experiments (N=7 to 17). Only F525N was found to significantly increase current density compared to wild-type (p=0.003).