![]() Figure 1 of
Bright, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1141-1150.
Figure 1 of
Bright, Mol Vis 2005;
11:1141-1150.
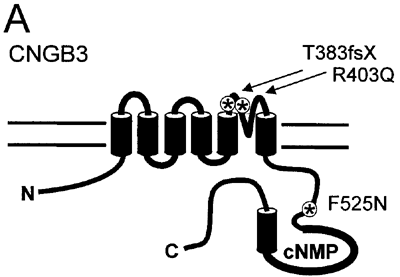
Figure 1. Disease-associated mutations in the CNGB3 subunit
A: A diagram shows the CNG channel subunit topology with approximate locations of CNGB3 mutations. B: A protein sequence alignment is shown of the P-loop region (the region of the subunit between the fifth and sixth transmembrane domains) containing the R403Q mutation (highlighted in red) for mammalian CNG channel subunits and the related bacterial potassium channel, MthK. The structural domains listed below this alignment are based on the known crystal structure of MthK [58]. "SF" refers to the selectivity filter. C: A protein sequence alignment is shown of the portion of the C-linker region (the intracellular region of the subunit between the 6th transmembrane domain and the cyclic nucleotide binding domain) containing the F525N mutation in CNGB3 (highlighted in red) for mammalian CNG channel subunits and the related hyperpolarization-gated, cyclic nucleotide-modulated channel, HCN2. The structural domains listed below this alignment are based on the known crystal structure of the carboxy-terminal region of HCN2 [45]. E', F' and A refer to specific α-helices within the HCN2 structure.
B:
hCNGB3 YLRCYYWAVRTLITIG GLPEP
bCNGB1 YIRCYYWAVKTLITIG GLPDP
hCNGA3 YIYSLYWSTLTLTTIG ETPPP
bCNGA1 YVYSLYWSTLTLTTIG ETPPP
rCNGA2 YIYCLYWSTLTLTTIG ETPPP
rCNGA4 YLYSFYFSTLILTTVG DTPLP
MthK WTVSLYWTFVTIATVGYGDYS P
-----------------
Pore helix SF
|
C:
hCNGB3 NFSIISKVDLFKGCDTQMIYDML
bCNGB1 NYSIVSKVALFQGCDRQMIFDML
hCNGA3 HLDTLKKVRIFQDCEAGLLVELV
bCNGA1 HLDTLKKVRIFADCEAGLLVELV
rCNGA2 HLSTLKKVRIFQDCEAGLLVELV
rCNGA4 HLSTLSRVQIFQNCEASLLEELV
mHCN2 CRKLVASMPLFANADPNFVTAML
------ ----- --------
E' F' A
|