![]() Figure 7 of
Chen, Mol Vis 2003;
9:735-746.
Figure 7 of
Chen, Mol Vis 2003;
9:735-746.
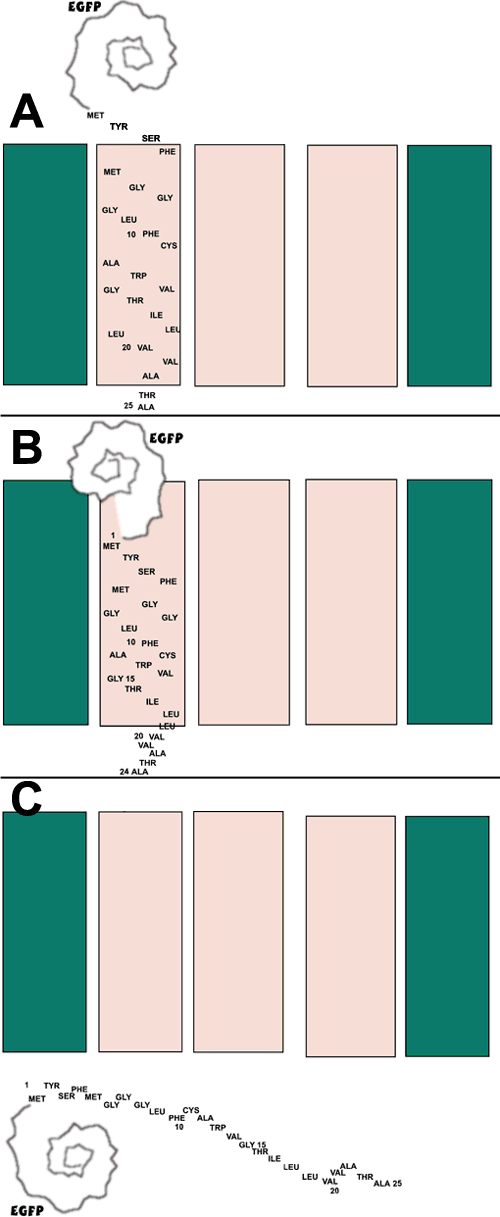
Figure 7. Possible topology of MP19-G25 in the cell membrane
A: Schematic of a proposed model of the MP19-25 truncation that contains EGFP fused to the NH2-terminal end of the fragment (GMP19-25). This model is not feasible due to the fact that this construct does not associate with the cell membrane. B: Another possible schematic showing the globular EGFP molecule integrated into the cell membrane. This is also not a possibility due to the fact that globular proteins do not integrate into the cell membrane, and our data indicate that the GMP19-25 fusion product does not associate with the membrane. C: The MP19-25 truncation peptide with EGFP fused to the NH2-terminal end cannot integrate into the cell membrane and thus must remain in the cytoplasm as a soluble protein.