![]() Figure 1 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2003;
9:584-593.
Figure 1 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2003;
9:584-593.
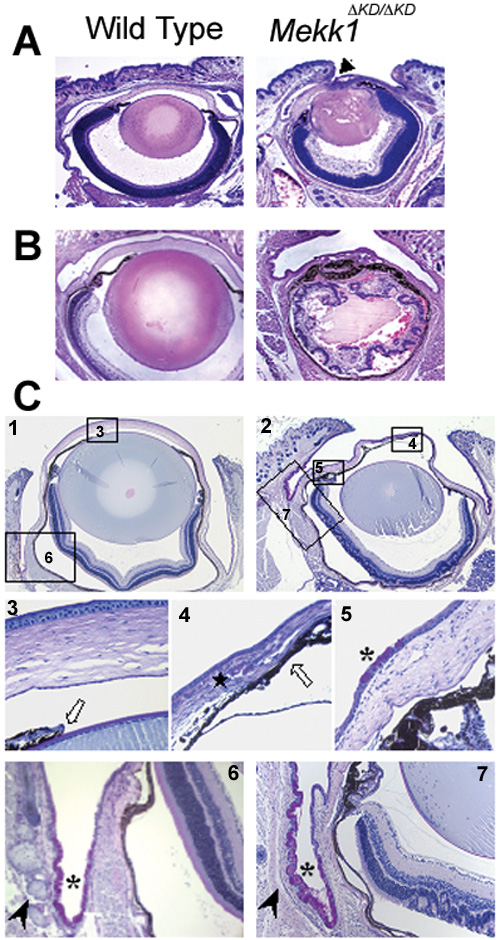
Figure 1. Eye pathology in postnatal stages of MEKK1 mutant mice
Coronal sections of wild type (left panels) and Mekk1ΔKD/ΔKD (right panels) mice at postnatal day 1 (A; P1) and day 10 (B; P10) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and photographed using light microscopy. Note the abnormal eye structures that occur in the Mekk1ΔKD/ΔKD as early as day one after birth (P1), including eyelid attachment to the cornea (arrowhead). More severe eye pathologies are associated with the homozygous mutant mice of older ages (P10). C: PAS stained coronal sections of paraffin-embedded eye tissues of wild type (1, 3, and 6) and Mekk1ΔKD/ΔKD (2, 4, 5, and 7) mice from postnatal day 27 (P27). Selected areas (3 through 7) are shown at higher magnification. Eye pathologies associated with the homozygous mutants, including smaller lens (1 and 2), impaired cornea morphology (1 through 5), irregular retina (6 and 7), overgrowth of the pigmented cells (3 and 4, white arrows). The mutants also completely lack Meibomian glands (6 and 7, arrowheads) and they show corneal stromal neovascularization (4, star) as well as goblet cell hyperplasia in cornea and conjunctiva (5, 6, and 7, asterisk).