![]() Figure 1 of
Qaddoumi, Mol Vis 2003;
9:559-568.
Figure 1 of
Qaddoumi, Mol Vis 2003;
9:559-568.
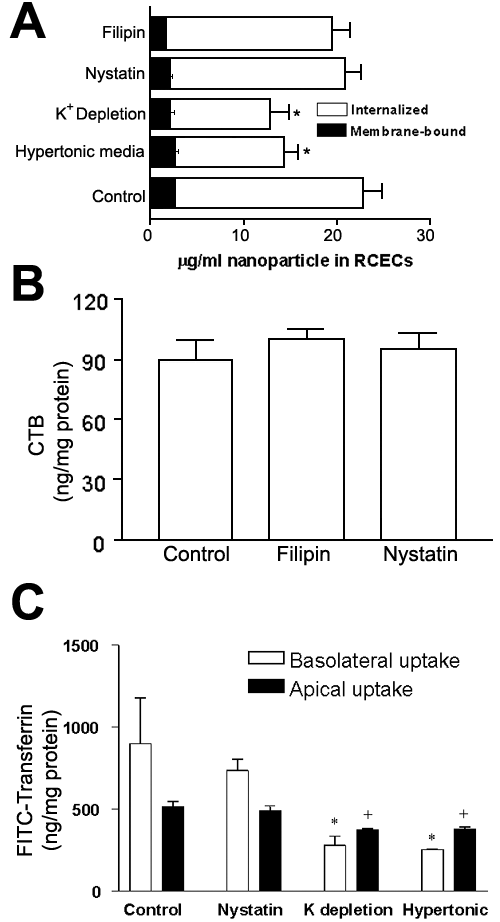
Figure 1. Effect of pharmacological treatments on internalization of PLGA nanoparticles, transferrin and cholera toxin B subunit in RCECs
A: Apical uptake of coumarin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles (0.5 mg/ml) in RCECs for 30 min at 37 °C under various treatments aimed at inhibiting endocytosis mediated by clathrin (K+ depletion and hypertonic challenge) or caveolae (nystatin and filipin). Membrane bound fractions were determined by centrifugation of the trypsinized cells 2 times following nanoparticle uptake and estimating the coumarin content in the solubilized pellet fraction. The asterisk denotes significant differences (p<0.05). B: Apical uptake of 5 μg/ml FITC-cholera toxin B subunit (CTB) in RCECs for 2 h at 37 °C under treatments aimed at inhibiting caveolae-mediated endocytosis. C: Apical and basolateral uptake of FITC-transferrin (50 μg/ml) in RCECs for 30 min at 37 °C under treatments aimed at inhibiting clathrin- or caveolae-mediated endocytosis. The asterisk denotes significant differences from both basolateral and apical uptake (p<0.05). The plus sign denotes significant differences from apical uptake (p<0.05). Bars represent mean±standard error of the mean (n=6).