![]() Figure 1 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2003;
9:301-307.
Figure 1 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2003;
9:301-307.
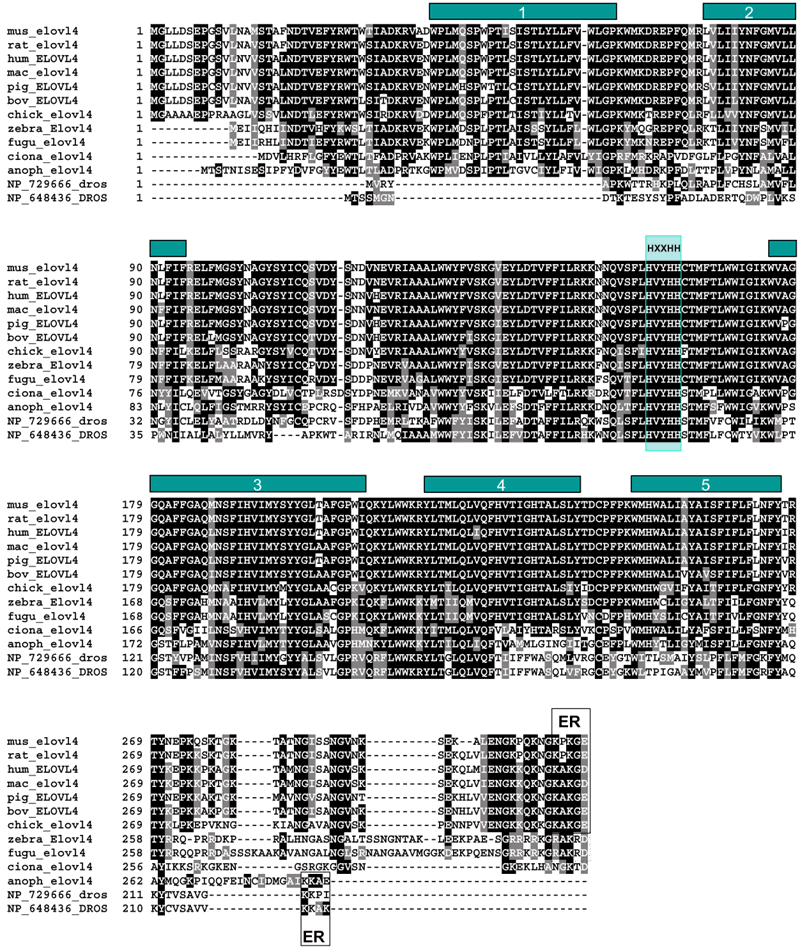
Figure 1. Comparison of Elovl4 amino acid sequences
Five putative transmembrane domains are indicated by bars 1-5. Carboxy-terminal dilysine signal KXKXX (vertebrates) or KKXX (invertebrates) presumably responsible for endoplasmic reticulum retention and the diiron-oxo binding HXXHH motif (His158-His162) are boxed. Residues printed in white on a black background are perfectly conserved in seven or more of the sequences shown. Residues printed in white on a gray background represent conservative substitutions (M=V=L=I, K=R=H, D=E, W=Y) in seven or more sequences shown. All other residues are printed in black on a white background. Note that in fugu and zebrafish C-termini, the ER motif is RXKXX (boxed with a broken line). Conserved residues are printed in white on black background. The sequences were derived from the following GenBank accession numbers: AF277093, mus_elovl4 (Mus musculus); the rat sequence rat_elovl4 (Rattus norvegicus) was derived from genomic contigs AC113258 (lacking exon 3) and AC126517 (lacking exon 5); NP_073563, hum_ELOVL4 (STGD3; Homo sapiens); AF461182, AB063100, mac_elovl4 (Macaca fascicularis); BU353103, chick_elovl4 (Gallus gallus); AK112719, ciona_elovl4 (Ciona intestinalis, sea squirt); the zebrafish (Danio rerio) sequence zebra_Elovl4 was derived from ESTs (BI706328, BI428673); EAA07022, anoph_Elovl4 (Anopheles gambiae str. PEST); NP_729666_dros and NP_648436_dros are two Drosophila melanogaster sequences, presumably elovl4 homologues.