![]() Figure 7 of
Wagner, Mol Vis 2002;
8:394-406.
Figure 7 of
Wagner, Mol Vis 2002;
8:394-406.
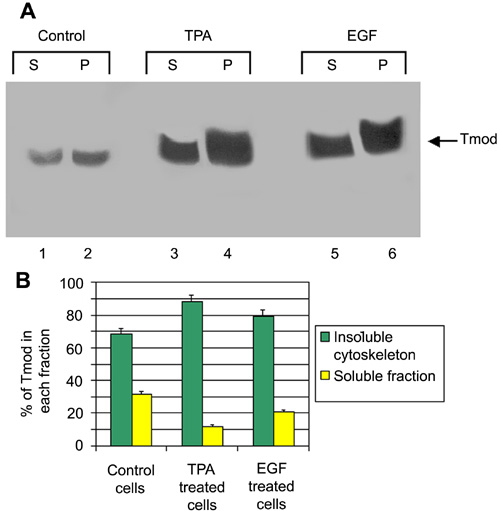
Figure 7. Tropomodulin phosphorylation by PKCα results in increased association of tropomodulin with the cytoskeleton
A: Control N/N 1003A cells or N/N 1003A cells treated with TPA or EGF were harvested in cold CSK buffer and centrifuged at 13,000 x g for 60 min at 4 °C. The resulting pellets containing insoluble, cytoskeleton-associated proteins and the resulting supernatants containing soluble proteins were loaded onto an SDS-PAGE gel (25 μg protein/lane) and the protein transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The nitrocellulose membrane was probed with anti-tropomodulin antibody. In control cells, 68.4% of the tropomodulin was in the insoluble, cytoskeleton-associated fraction (lane 1 versus lane 2). In TPA-treated cells, 88.1% of the tropomodulin was in the insoluble, cytoskeleton-associated fraction leaving only 11.9% of the tropomodulin in the soluble fraction (lane 3 versus lane 4). Cells treated with EGF showed that 79.2% of the tropomodulin was in the insoluble, cytoskeleton-associated fraction leaving only 20.8% of the tropomodulin in the soluble fraction (lane 5 versus 6). S designates the supernatant pellet. P designates the Triton-insoluble pellet fraction. B: Graphical representation of cytoskeleton-associated tropomodulin. There was a significant difference in the amount of cytoskeleton-associated tropomodulin between control, TPA-treated cells, and EGF-treated cells (p<0.05).