![]() Figure 1 of
Smith, Mol Vis 2002;
8:26-31.
Figure 1 of
Smith, Mol Vis 2002;
8:26-31.
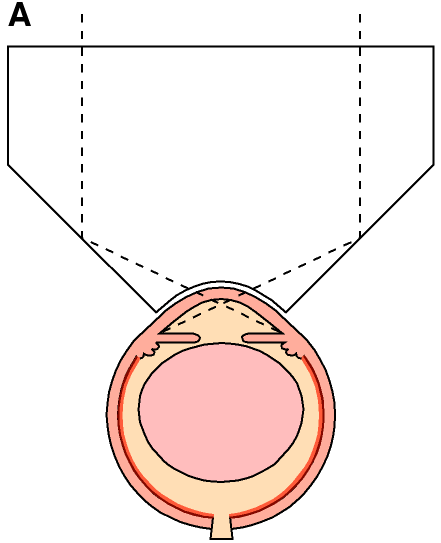
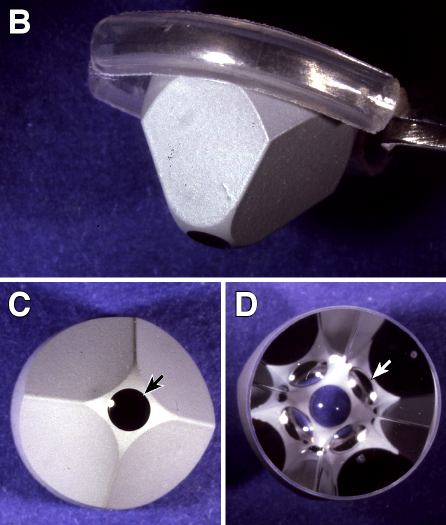
Figure 1. Design of goniolens
A: Schematic of mouse goniolens on an eye. The observer views the eye through the plano surface of the lens. The dotted lines trace the image path. The angled surfaces of the lens direct light into the anterior chamber angle. The corneal surface of the lens is directly tangent to the cornea and separated from it only by the tear film. B: Goniolens held in forceps that are modified by covering the gripping surface with polyethylene tubing. C: Corneal surface of goniolens (arrow). All other portions of the goniolens seen from this surface are silvered D: Plano surface of goniolens. The four mirrors of the lens are visible as darker semicircles adjacent to the corneal contact lens (white arrow points to one). The corneal contact lens is the central area that appears blue because of the background.