![]() Figure 3 of
Lyubarsky, Mol Vis 2001;
7:71-78.
Figure 3 of
Lyubarsky, Mol Vis 2001;
7:71-78.
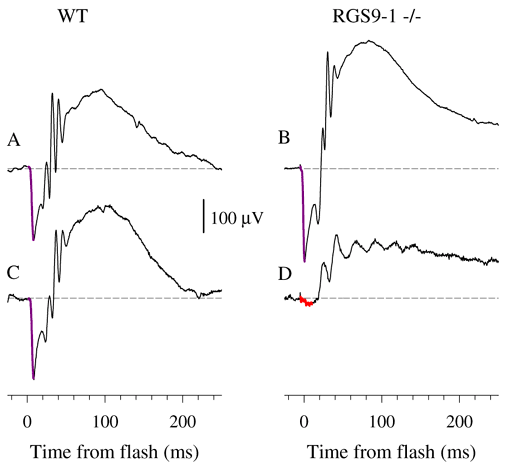
Figure 3. ERGs from WT and RGS9-1 -/- mice
A white flash isomerizing ~1% of the rhodopsin in the retina was delivered in a ganzfeld to each dark-adapted animal, generating responses seen in panels A and B. The response to the same flash was then recorded again after 2 min in darkness (panels C and D). The initial corneal-negative component highlighted in violet in panels A-C and in red in panel D is the a-wave, while the corneal-positive deflections that follow (and truncate) the a-wave are a mixture of rod- and cone-driven b-waves and the so-called oscillatory potentials [29].