![]() Figure 1 of
John, Mol Vis 2000;
6:204-215.
Figure 1 of
John, Mol Vis 2000;
6:204-215.
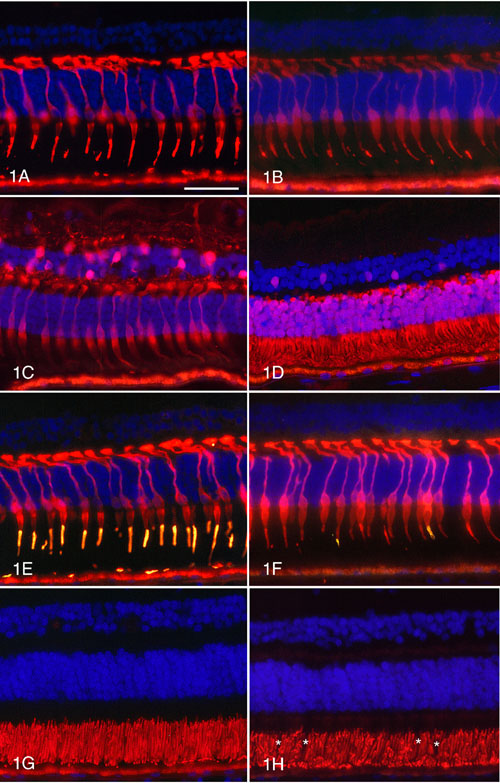
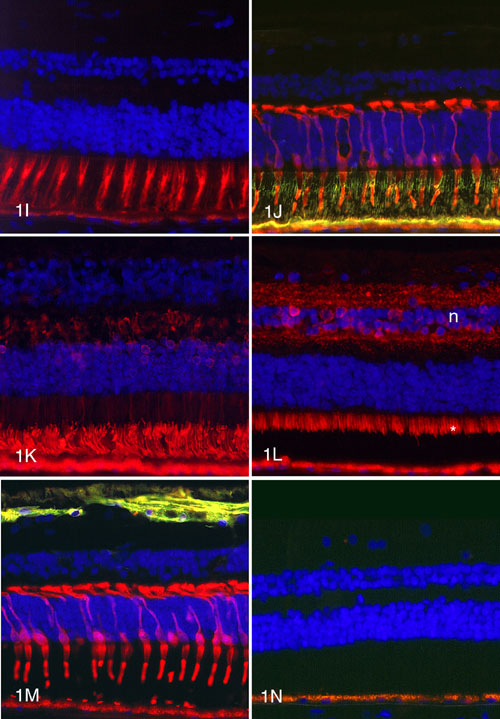
Figure 1. Immunocytochemical labeling of normal human retinas
A. Antibody 7G6 produces labeling of the outer segments and cytoplasm of the inner segments, cell bodies and synapses of all cone photoreceptors. B. Anti-X-arrestin labels the outer segments and the cytoplasm of the cell bodies and synapses of all cones. C. Anti-calbindin labels the cytoplasm of the cone inner segments, cell bodies and synapses. The horizontal cells and some bipolar and amacrine cells are also labeled. D. The outer segments and cytoplasm of the cones and rods are positive with anti-recoverin. A population of cone bipolar cells is also recoverin-positive. E. All cones are positive with antibody 7G6 (red) and the majority of cone outer segments are positive (gold) for red/green cone opsin. F. All cones are 7G6-positive (red) and a few cone outer segments (gold) are blue cone opsin-positive. G. The cone and rod outer segments are positive with anti-peripherin-2. H. The rod outer segments are rhodopsin-positive but the cones (*) appear as negative images. I. The extracellular cone sheaths are uniform in structure and PNA-positive (red). J. The interphotoreceptor matrix is positive for IRBP (green). All cones are labeled (red) with 7G6. K. The rod outer segments are strongly labeled (red) with anti-rod arrestin. Some rod cell bodies and synapses are weakly positive. L. Mitochondria in the cone and rod inner segments (*) are positive for cytochrome C oxidase. The inner and outer plexiform layers and some cells in the inner nuclear layer (n) are also labeled. M. Labeling with anti-GFAP (green) is restricted to astrocytes and Müller end feet. The cones are labeled (red) with 7G6. N. Control section treated with no primary antibody shows only autofluorescent lipofuscin granules in the RPE.
Autofluorescent lipofuscin is present in the retinal pigment epithelium at the bottom of the panels. The scale bar represents 50 mm.