![]() Figure 4 of
Winkler, Mol Vis 1999;
5:32.
Figure 4 of
Winkler, Mol Vis 1999;
5:32.
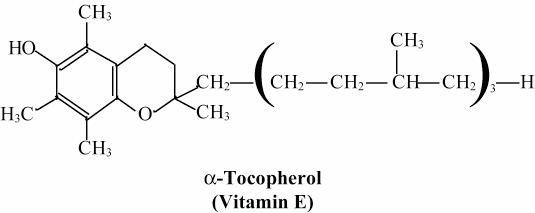
Figure 4. Basic properties and structure of vitamin E
Keys facts regarding vitamin E and its role as a scavenger of free radicals; the structure of vitamin E.
* A group of eight fat-soluble compounds
* a-tocopherol is the biologically most active form
* Absorbed into lymphatics from the intestines
* Protects lipids from peroxidative damage
* A chain-breaking antioxidant that reacts with ·O2-, 1O2, peroxyl (ROO·), and alkoxyl (RO·) radicals
* Major lipid-soluble antioxidant protecting membranes and lipoproteins from injury
* Vitamin E· (radical form) is reduced back to Vitamin E by Vitamin C