Figure 7. Examples of functional testing in the anole lizard. A: This image shows an histological section through the normal fovea structure. B: An histological section through an anole retina one month after laser burn injury to the choroid beneath the fovea (red
arrowheads). C: Optokinetic tracking comparing wild-type anoles to those with laser injury, showing a significant decrease in the spatial
frequency threshold (*p<0.001, n=5). D: Live bait capture setup where an anole is kept behind a door in a Perspex box and then given access to a single cricket
to capture (red dot). Groups of 8 anoles were fasted for between 1 and 5 days, and the number of crickets captured is recorded
in the bar chart (E). By 5 days of fasting, all 8 wild-type anoles (black bars) caught the bait, but the injured anoles (grey bars) captured
significantly less bait (*p < 0.05, n = 8). The white bars indicated how many of the 8 anoles in the test did not catch the
bait.
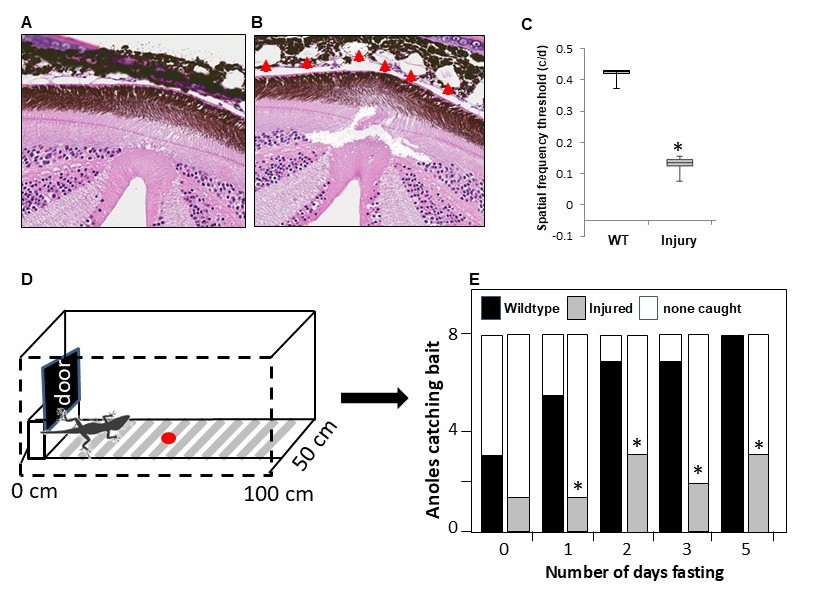
 Figure 7 of
Gregory-Evans, Mol Vis 2025; 31:319-343.
Figure 7 of
Gregory-Evans, Mol Vis 2025; 31:319-343.  Figure 7 of
Gregory-Evans, Mol Vis 2025; 31:319-343.
Figure 7 of
Gregory-Evans, Mol Vis 2025; 31:319-343. 