Figure 2. Targeted PCR amplification using DNA extracted from archival and fresh DNA samples is shown for comparison. Targeted PCR amplification
of canine (A) and feline (B) RHO was performed. C: Targeted PCR amplification was carried out for rhesus RHO (rRHO) and RPGR, as well as human RHO (hRHO), using DNA extracted from archival epoxy resin-embedded rhesus samples (MR1–MR2). M-100 denotes the marker. D: Targeted PCR amplification of canine GUSB1, AMPD2, REEP1, and PRCD was performed using DNA extracted from archival epoxy resin-embedded canine samples (CLF1–CLF5). CLF4 represents
canine cornea DNA (epoxy resin extraction). CLF5 represents canine DNA from epoxy resin extraction of (a) cornea and (b) retina.
CLF, canine DNA from blood; FC, feline DNA from buccal swab; NC, non-template control. Note that the PCR aimed at non-species-specific
targets for the primers failed. E: The electropherogram shows reads of PCR amplifications (RHO) from DNA extractions from dog cornea (top) and rhesus macaque
retina (bottom).
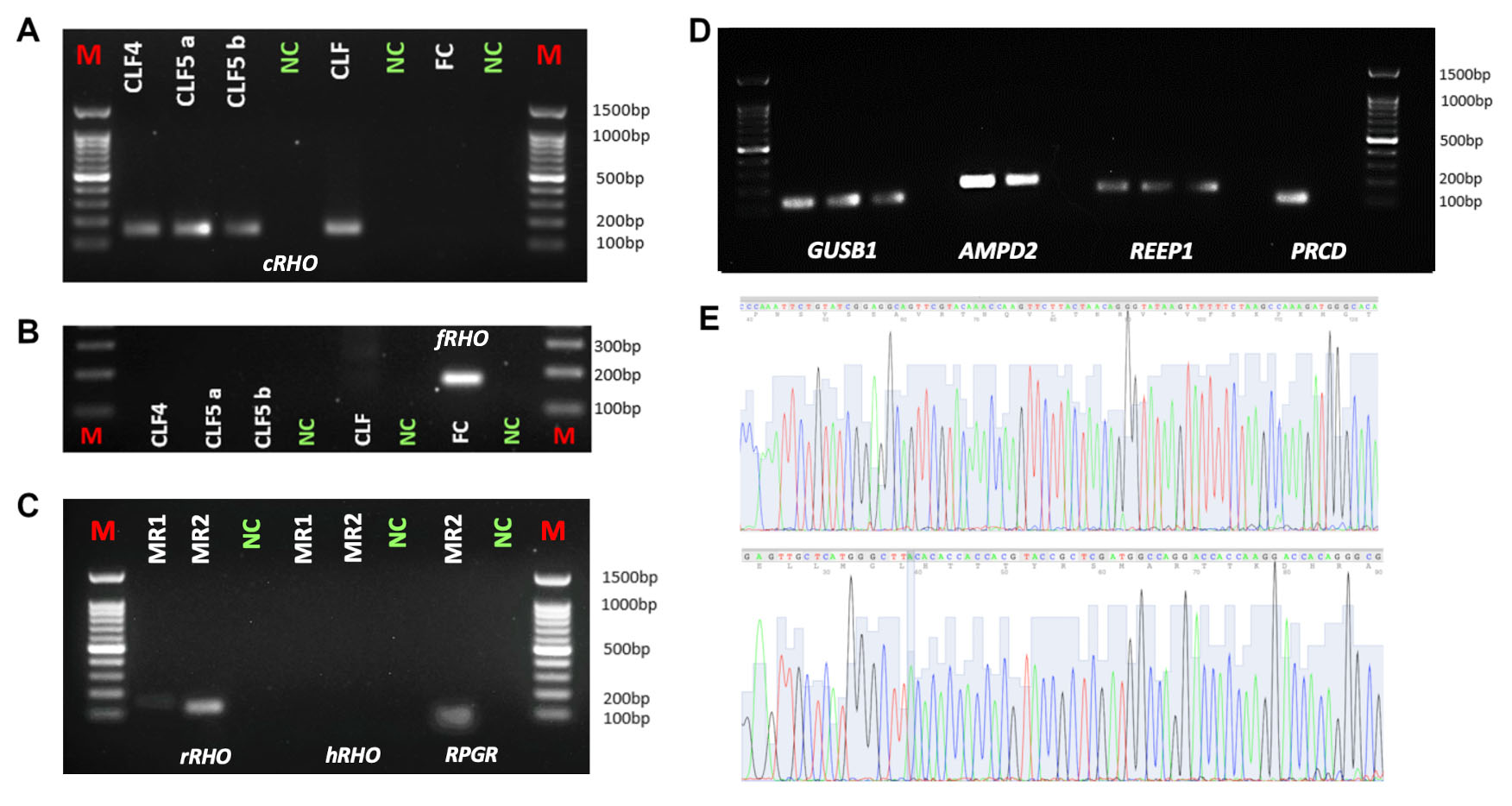
 Figure 2 of
Niggel, Mol Vis 2025; 31:297-304.
Figure 2 of
Niggel, Mol Vis 2025; 31:297-304.  Figure 2 of
Niggel, Mol Vis 2025; 31:297-304.
Figure 2 of
Niggel, Mol Vis 2025; 31:297-304. 