Figure 1. Slit-lamp and IVCM images of MCD patients with different CHST6 mutation types. Slit-lamp and sequential in vivo confocal images
of a healthy subject (A-control) and selected MCD patients (B–F), representing different corneal layers. Marked corneal layers are the suprabasal epithelium, BE, Bowman’s layer (BL), region
immediately before anterior stroma, anterior stroma, middle stroma, posterior stroma, and endothelium. A slit-lamp and sequential
IVCM analysis of the control eye showed normal cellular morphology of the different corneal layers. Suprabasal epithelium,
BE of MCD patients - B, C, and F show scattered deposits and slightly altered nerve fibers (NF); D with cluster of deposits and loss of NF; and patient E (MCD patient with ORF deletion) shows clumps of deposits with scar
tissue (S) and loss of NF. BL and region next to the anterior stroma of patients B and F show deposits along with loss of
NF; Patients C, and D show confluent, clumps of deposits with scar tissue (S); Patient E showed clumps of highly reflective
homogenous granular deposits with the rupture of basement membrane and loss of BL resulting in scar tissue. The endotheliums
of Patients B and F show scattered deposits; Patients C, D, and E showed deposits along with polymegathism. Homogenous reflective
material with dark striae (St)-like images was observed throughout the stroma (for patients B-F). Striae-like observations were not clearly visible due to the highly light-reflective clumps of deposits (E). Clinical and IVCM analysis across the corneal thickness of MCD patients 17 (C), 29 (D), and 60–1 (E) carrying fs deletion (del), deletion-insertion (delins), and deletion of ORF mutations, respectively, revealed severe scars
in the BL and anterior stroma due to highly light-reflective clumps of deposits presenting severe corneal morphological alterations.
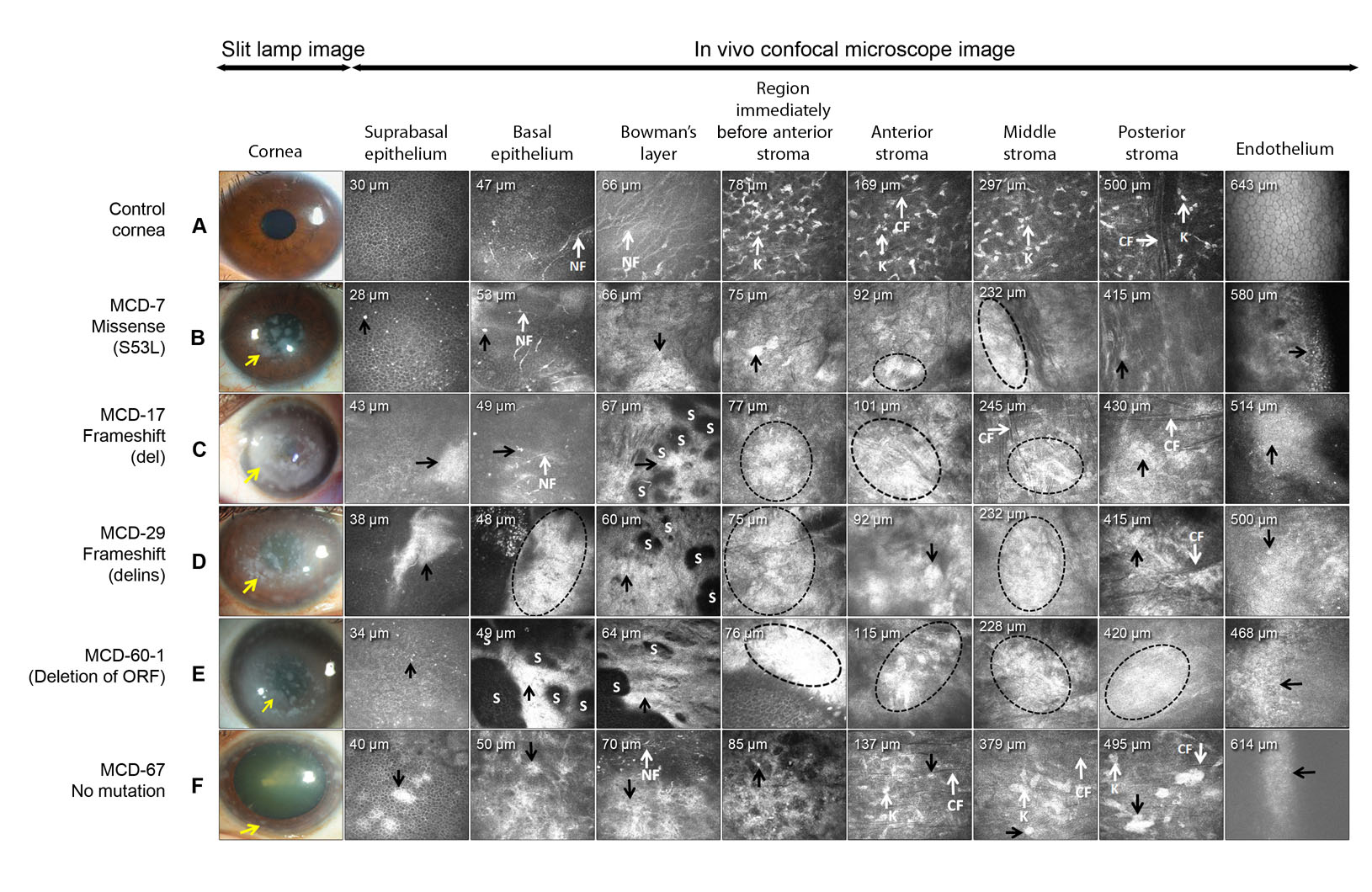
 Figure 1 of
Murugan, Mol Vis 2024; 30:305-318.
Figure 1 of
Murugan, Mol Vis 2024; 30:305-318.  Figure 1 of
Murugan, Mol Vis 2024; 30:305-318.
Figure 1 of
Murugan, Mol Vis 2024; 30:305-318. 