Figure 3. C5a and LPS-induced inflammatory mediators were suppressed in the presence of R9-SOCS3-KIR. A: The ARPE-19 cells were seeded in six-well plates and grown overnight. They were placed in serum-free media and treated with
or without R9-SOCS3-KIR (20 μM) for 1 h, followed by treatment with C5a peptide (50 ng/ml) for 4 h. Quantitative RT-PCR was
conducted using the primers for the target genes indicated, and β-actin primers served as the internal control. The results
represent the average of biologic triplicates, and the error bars indicate the standard deviations. B: The anti-inflammatory effects of R9-SOCS3-KIR were observed in LPS-treated J774A.1 cells. The mouse macrophage, J774A.1
cells, were grown overnight in 12-well plates. They were placed in serum-free media and treated with R9-SOCS3-KIR (20 μM)
for 1 h, followed by the addition of LPS (1 μg/ml) for 4 h. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed using primers for the target
genes indicated, and β-actin primers served as the internal control. The bars represent the average of the triplicates ± standard
deviation. For each comparison, statistical significance was assessed using the Student’s t-test. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. C. J774A.1 cells in 1% FBS-containing media were treated with R9-SOCS3-KIR or the control peptide (at 20 μM) for 1 h, followed
by treatment with C5a (50 ng/ml), and incubated overnight. The supernatants were harvested and used to quantify VEGF-A using
an ELISA kit from PeproTech. ****, p < 0.0001, as determined by one-way ANOVA.
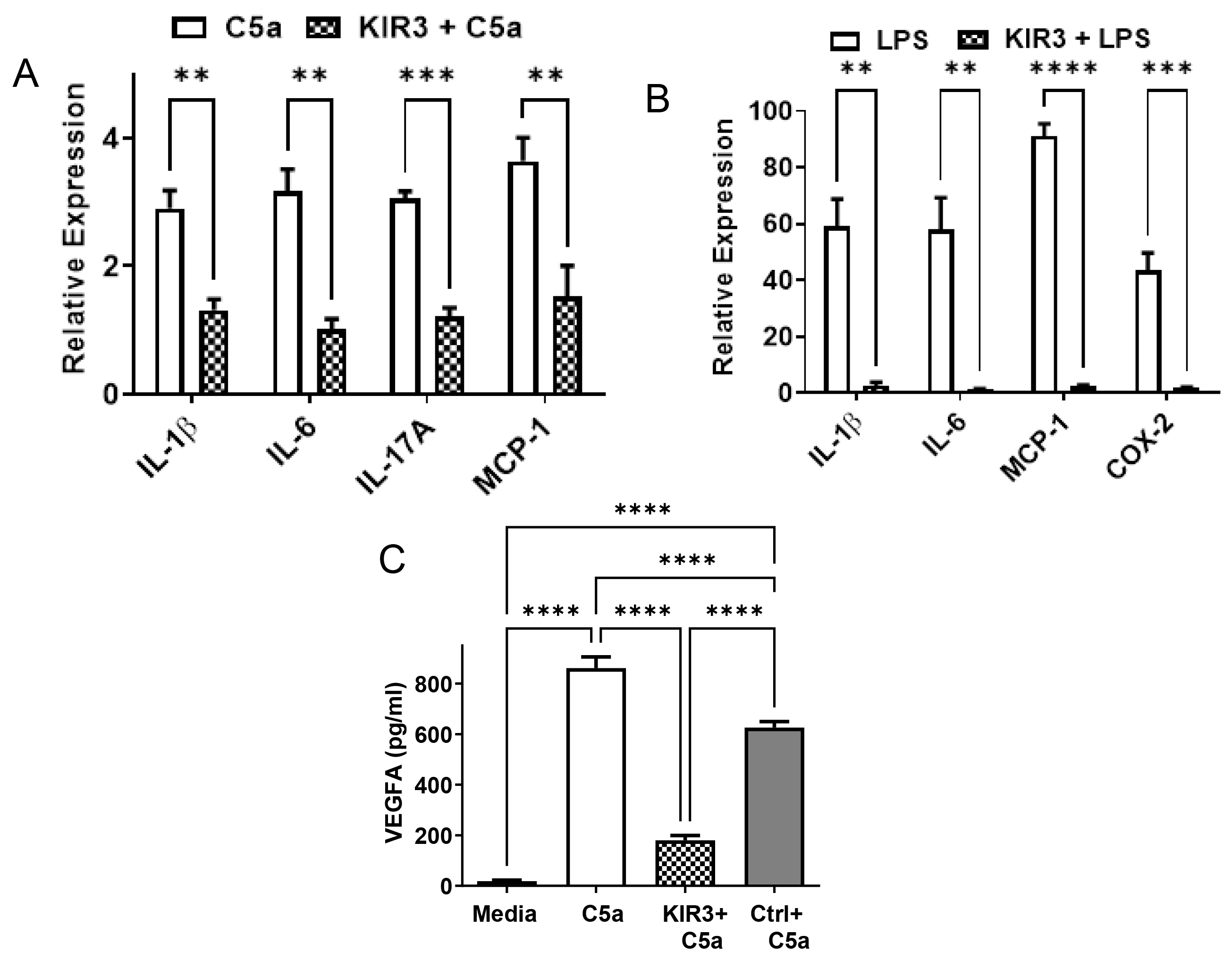
 Figure 3 of
Ahmed, Mol Vis 2023; 29:338-356.
Figure 3 of
Ahmed, Mol Vis 2023; 29:338-356.  Figure 3 of
Ahmed, Mol Vis 2023; 29:338-356.
Figure 3 of
Ahmed, Mol Vis 2023; 29:338-356. 