Figure 3. General workflow of the study. The genetic and phenotypic information collected from a well-defined retrospective cohort of
ABCA4 retinopathy patients provided a list of ABCA4 missense variants, allowing us to test the protein structure–based computational pathogenicity prediction platform. Our analysis
methods included physically comparing WT and mutant proteins based on observable structural changes between the AF2 WT and
variant models, evaluating thermodynamic stability, examining changes in inter- and intramolecular binding/interaction, surface
properties, and solvent accessibility, mainly using experimental structures. In conjunction with other in silico pathogenicity
prediction methods, these analyses can aid in understanding the genotype–phenotype association in ABCA4-related inherited retinal diseases and in classifying VUS.
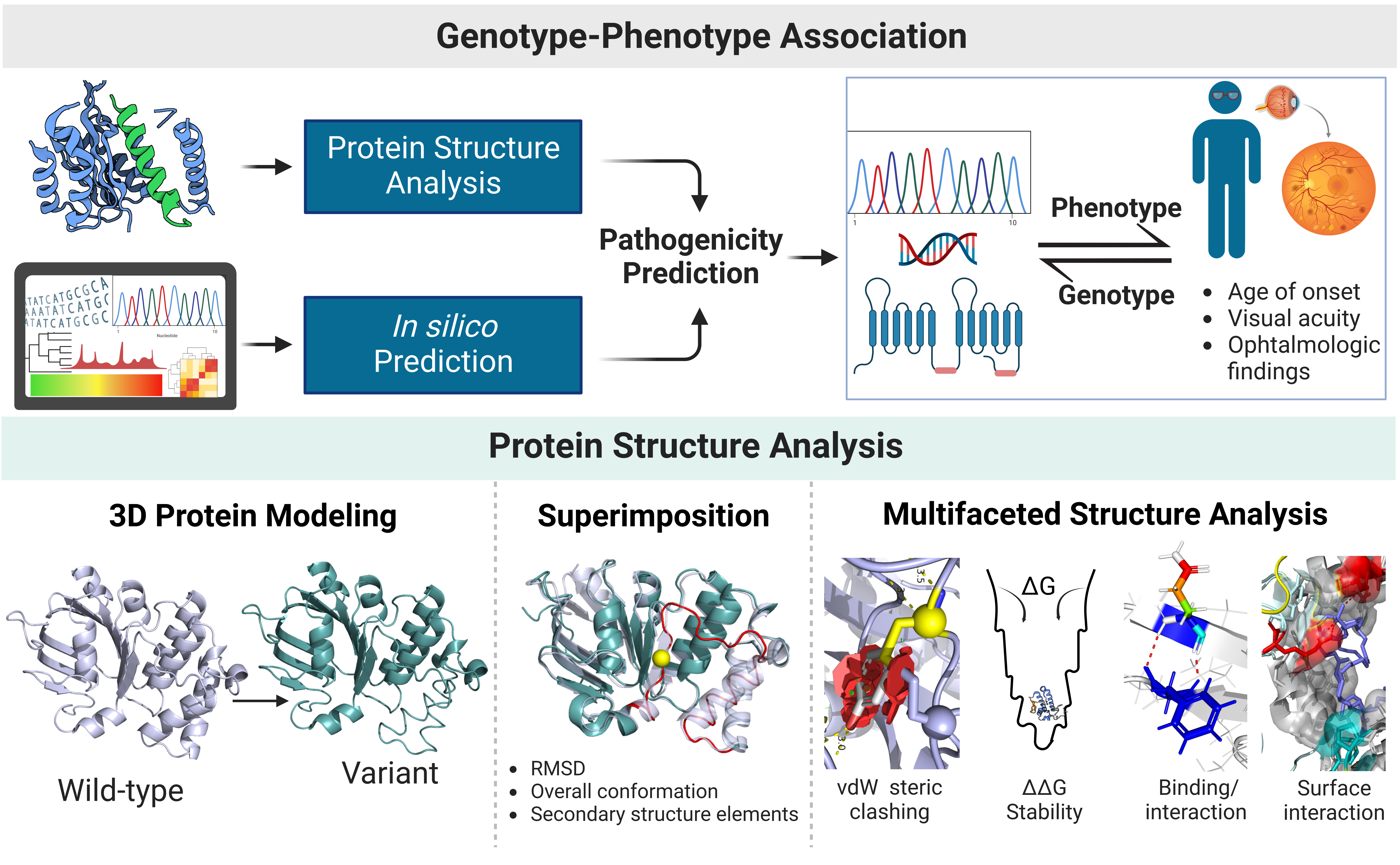
 Figure 3 of
Cevik, Mol Vis 2023; 29:217-233.
Figure 3 of
Cevik, Mol Vis 2023; 29:217-233.  Figure 3 of
Cevik, Mol Vis 2023; 29:217-233.
Figure 3 of
Cevik, Mol Vis 2023; 29:217-233. 