Figure 6. The patient had ABCA4-associated autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy (arCORD). A: This clinical phenotype was initially more suggestive of disseminated chorioretinitis, showing widespread peripheral punched-out
chorioretinal lesions. However, the patient carried a childhood diagnosis of Stargardt disease, which had not been genetically
confirmed. Broad NGS-based sequencing led to the identification of two previously reported ABCA4 mutations, with phase determination confirming them to be in trans, consistent with ABCA4-associated arCORD. B: Upon further examination, the patient's clinical phenotype demonstrated characteristic peripapillary sparing (green arrow)
and far peripheral hyper-autofluorescent flecks (white arrow), which are typical of an ABCA4-associated phenotype.
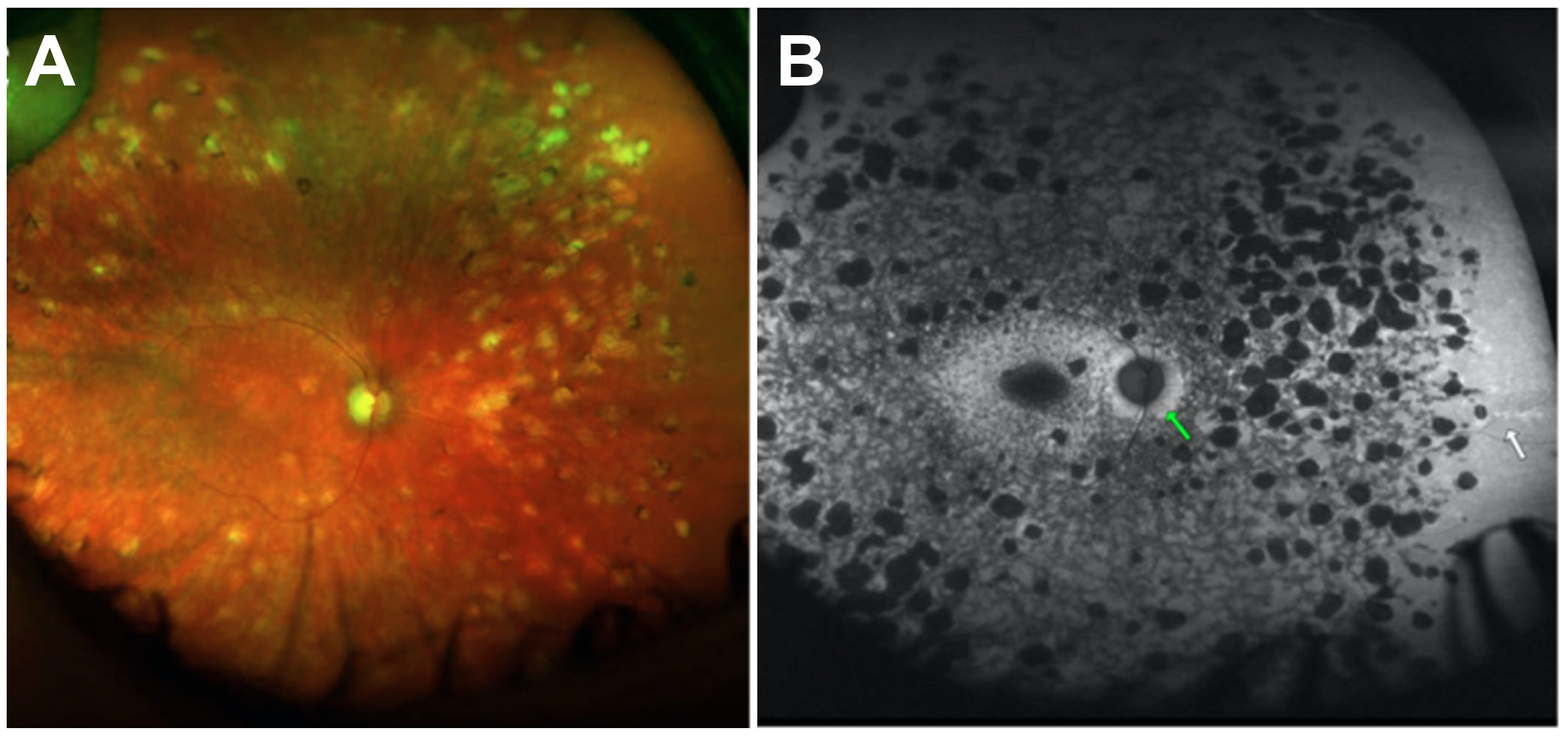
 Figure 6 of
Gupta, Mol Vis 2022; 28:203-219.
Figure 6 of
Gupta, Mol Vis 2022; 28:203-219.  Figure 6 of
Gupta, Mol Vis 2022; 28:203-219.
Figure 6 of
Gupta, Mol Vis 2022; 28:203-219. 