Figure 7. Quercetin alleviated lacrimal gland inflammation caused by AQP5 deficiency. A: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining showed morphological changes. CD4+: Immunofluorescence staining of CD4+ demonstrated CD4+ T cells (red: CD4+, blue: 4’6-diamidino-2-phenylindole [DAPI]). Ly6g: Immunofluorescence staining of Ly6g showed neutrophils (red: Ly6g, blue:
DAPI). F4/80: Immunofluorescence staining of F4/80 showed macrophages (red: F4/80, blue: DAPI). B: ImageJ immunofluorescence profile analysis showed the CD4+ positive score, Ly6g positive score, and mean fluorescence intensity of F4/80 (n = 6 samples). C: Immunofluorescence staining of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) showed myoepithelium morphology (green: α-SMA, blue: DAPI),
and ImageJ and GraPade were used to compute the result (n = 6 samples). D: Western blotting showed the expression level of α-SMA and GAPDH (n = 3 samples). E: Real-time PCR exhibits expression of chemokine and proinflammatory factors (n = 3 samples). F: The lacrimal secretion of AQP5−/− mice was measured using the phenol red cotton thread method. G: Sodium fluorescein staining in the cornea. *p<0.05, **p<0.001. Independent sample t test. Scale bars: (A): 100 μm, 40 μm. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.0001.
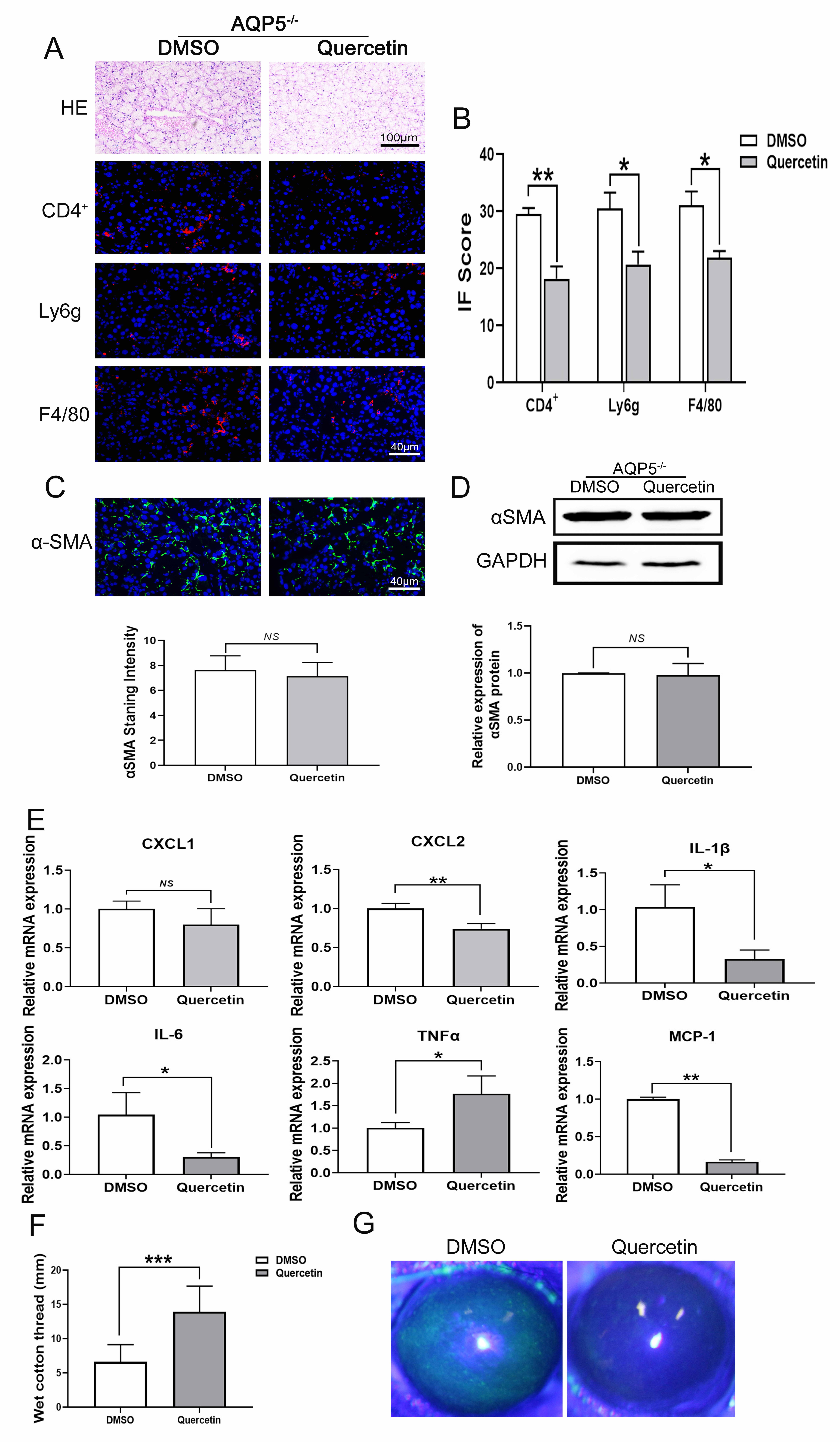
 Figure 7 of
Hu, Mol Vis 2021; 27:679-690.
Figure 7 of
Hu, Mol Vis 2021; 27:679-690.  Figure 7 of
Hu, Mol Vis 2021; 27:679-690.
Figure 7 of
Hu, Mol Vis 2021; 27:679-690. 