Figure 3. Disease-causing mutations of dynein heavy chain domains. A: DYNC1H1. DD, dimerization domain; DIC and DLIC are regions of interaction; the stalk specifies the area of microtubule binding.
ATPase domains 1–6 (blue bars 1–6) are shown. Top, human mutations. Mutations causing intellectual disability (red); MCD (black);
SMA-LED (blue). Bottom, mouse and zebrafish mutations. Green arrow, point of DYNC1H1 truncation in the linker region produced
in the Six3Cre conditional knockout (retDync1h1−/−). B: DYNC2H1. Mutations associated with short-rib polydactyly syndrome (black) and nonsyndromic retinitis pigmentosa (RP; red)
are indicated. C: Partial sequences of human Dync2h1 exons 63 and 65 flanking exon 64 (green) present only in isoform 2. A stop codon pS3279*
is associated with nonsyndromic recessive RP.
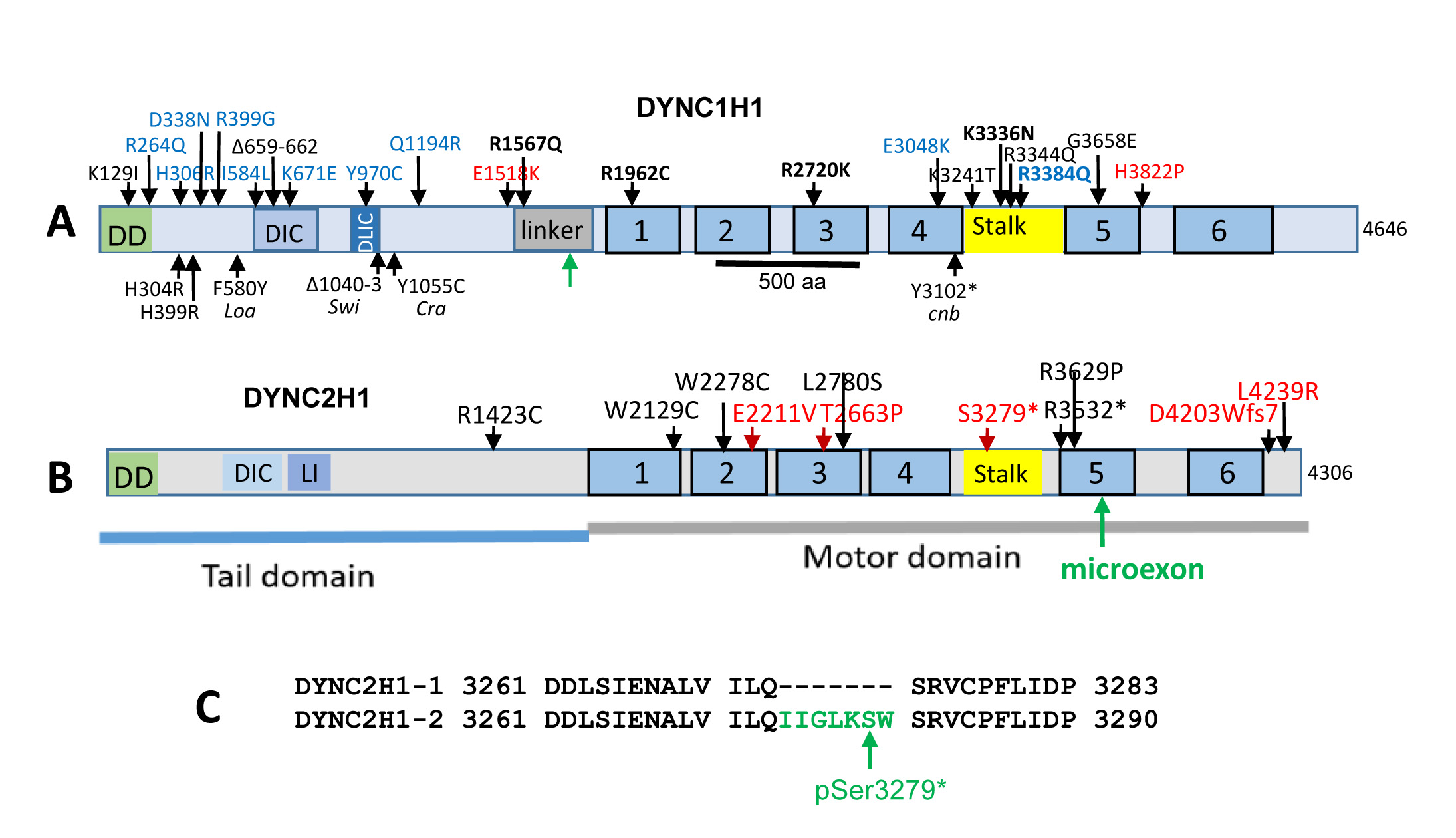
 Figure 3 of
Dahl, Mol Vis 2021; 27:506-517.
Figure 3 of
Dahl, Mol Vis 2021; 27:506-517.  Figure 3 of
Dahl, Mol Vis 2021; 27:506-517.
Figure 3 of
Dahl, Mol Vis 2021; 27:506-517. 