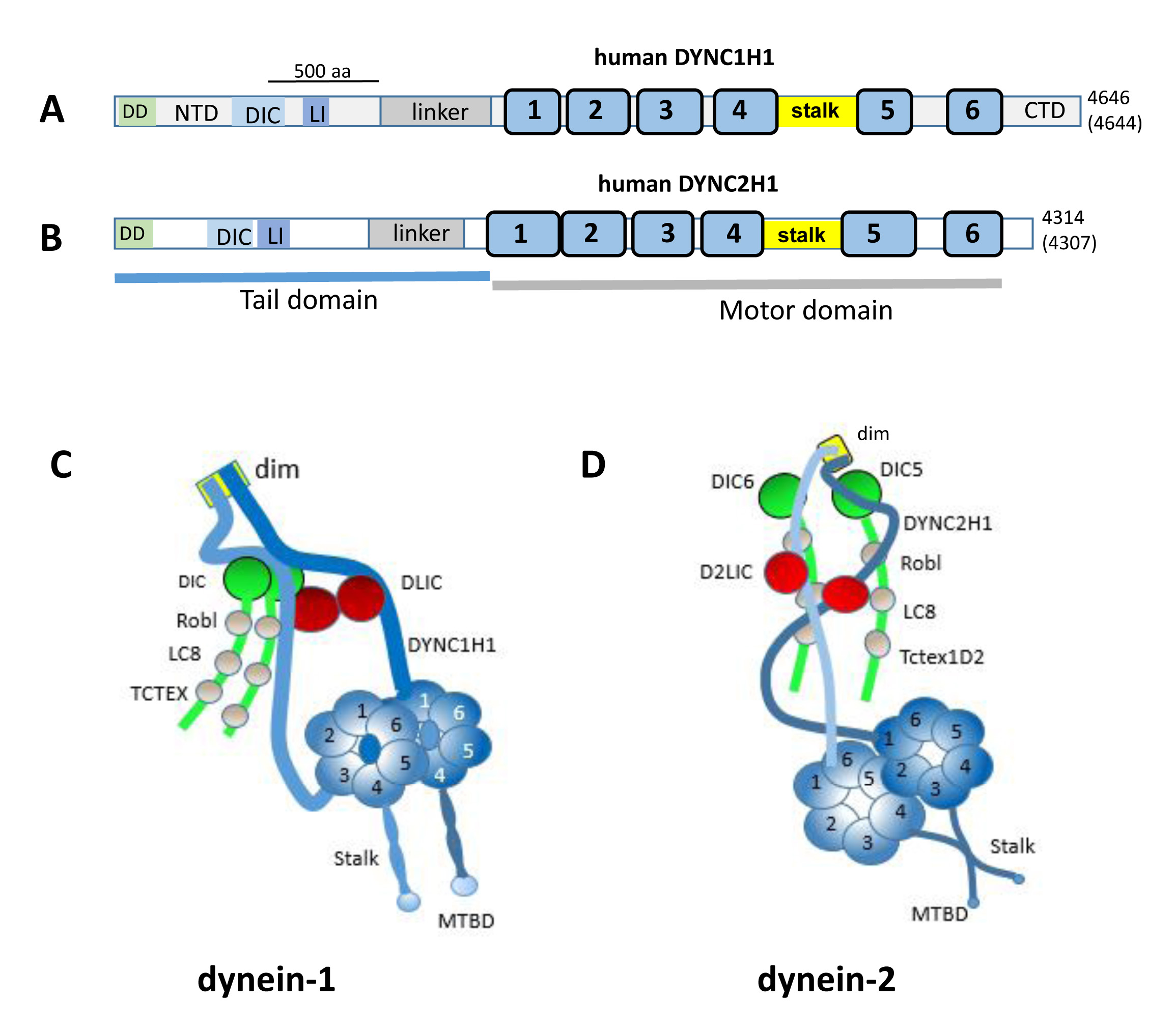
Figure 1. Human dynein-1 and dynein-2.
A, B: Schematic representation of human dynein heavy chain DYNC1H1 (
A) and DYNC2H1 (
B) domain structures. DD, dimerization domain; NTD, N-terminal domain; DIC, dynein intermediate chain interaction site; LI,
light intermediate interaction site; blue bars, ATPase domains 1–6; stalk; MBD, microtubule-binding domain; CTD, C-terminal
domain. Numbers at the C-terminus indicate amino acids in the human and mouse, with those of the mouse enclosed by parentheses.
Adapted from [
88] and [
59]. The 500 aa bar indicates the length occupied by 500 amino acids.
C, D: representations of multimeric dynein-1 and dynein-2. The heavy chains form homodimers, the scaffolds of which organize the
distributions of intermediate, light intermediate, and light chains (adapted from [
45] and [
33]. The N-terminal 200 amino acids represent the dimerization domain (dim).
 Figure 1 of
Dahl, Mol Vis 2021; 27:506-517.
Figure 1 of
Dahl, Mol Vis 2021; 27:506-517.  Figure 1 of
Dahl, Mol Vis 2021; 27:506-517.
Figure 1 of
Dahl, Mol Vis 2021; 27:506-517.