Figure 1. AMCM inhibited synthesis and secretion of chemokines and reduced innate immune receptors transcription in poly I:C–stimulated
HLMs. A: As expected, polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid sodium salt (poly I:C) stimulation statistically significantly induced synthesis
of the CCL2, CCL5, and CXCL10 chemokines, which was significantly inhibited by amniotic membrane conditioned medium (AMCM).
B: Similarly, poly I:C stimulation statistically significantly induced secretion of CCL2, CCL5, and CXCL10 chemokines, which
was statistically significantly inhibited by AMCM. C: Poly I:C stimulation statistically significantly induced synthesis of MDA5, RIG-1, and TLR3 innate immune receptors, which
was statistically significantly inhibited by AMCM. Bars represent the mean ± standard error (SE); *p<0.5; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001;
n.s.: no statistical difference. All assays were performed three times in triplicate.
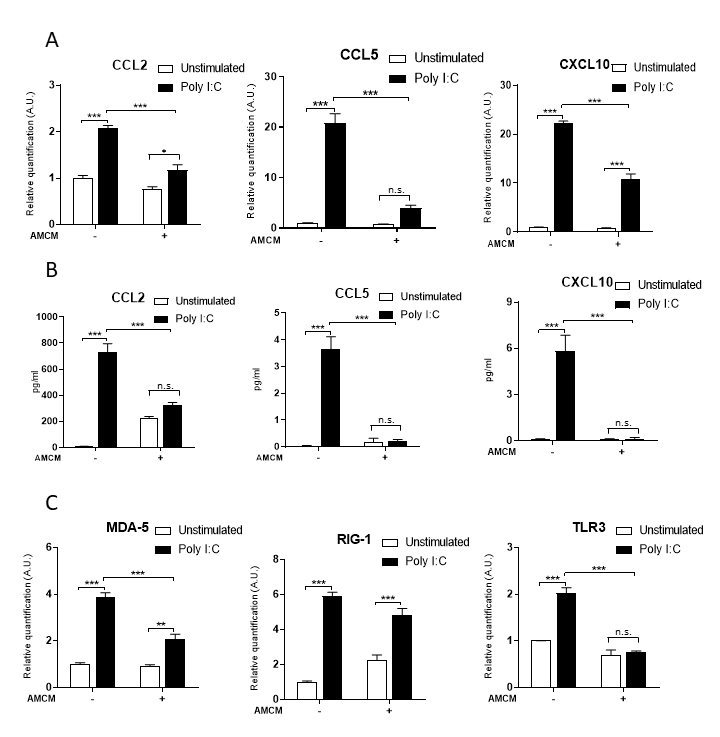
 Figure 1 of
Domínguez-López, Mol Vis 2021; 27:370-383.
Figure 1 of
Domínguez-López, Mol Vis 2021; 27:370-383.  Figure 1 of
Domínguez-López, Mol Vis 2021; 27:370-383.
Figure 1 of
Domínguez-López, Mol Vis 2021; 27:370-383. 