Figure 1. Major clinical features of the investigated corneal diseases. In long-standing bullous keratopathy, the cornea becomes edematous
and opaque. In the final stage newly formed vessels (arrow) penetrate the corneal tissue (A). In advanced forms of Fuchs' dystrophy the normal hexagonal endothelial cell monolayer on the posterior corneal surface
is altered with a decrease in cell number (arrow), concomitant stromal edema and thickening (B). Stromal degeneration (arrow) after HSV infection. Some newly formed peripheral stromal vessels are also present (C).
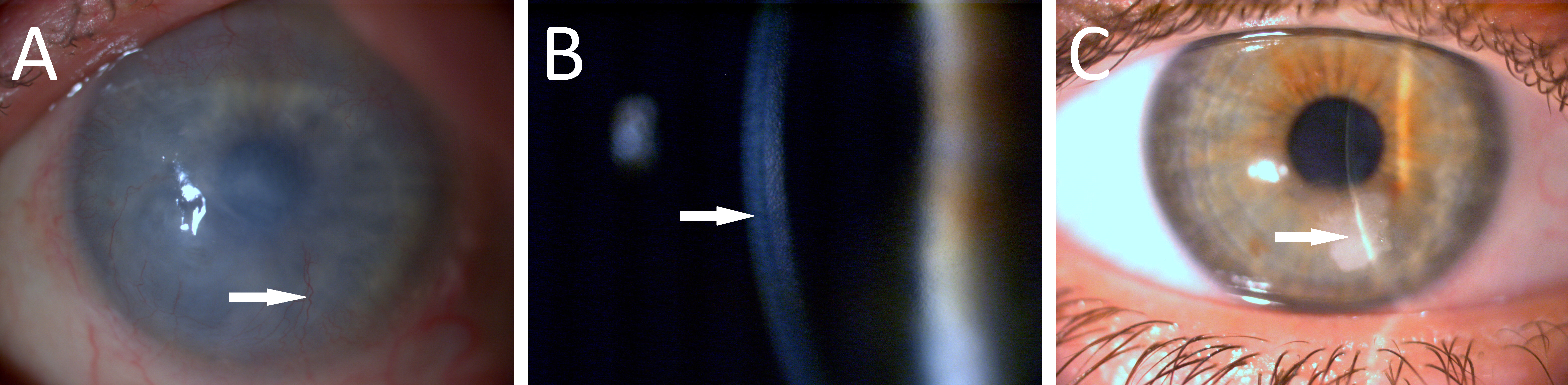
 Figure 1 of
Módis, Mol Vis 2021; 27:26-36.
Figure 1 of
Módis, Mol Vis 2021; 27:26-36.  Figure 1 of
Módis, Mol Vis 2021; 27:26-36.
Figure 1 of
Módis, Mol Vis 2021; 27:26-36. 