Figure 3. Protection against RGC and retinal tissue damage following treatment with KIOM-2015E. SD rats were treated using topical eye
drops (E.D., thrice daily) or via oral administration (P.O., once daily) of KIOM-2015EW, KIOM-2015EE, or Ginexin-F. Five days
after treatment, retinal tissues were analyzed via hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) staining and TUNEL assays after vertical
sectioning. A: Significantly fewer RGCs were observed in the GCL of rats in the MCAO+vehicle group than in those of the sham-operated group.
However, treatment with KIOM-2015E suppressed the loss of RGC. Quantitative analysis of RGC number in the GCL. Five pictures
were randomly selected per group. The graph displays the average numbers of RGCs. B: Retinal sections were subjected to a TUNEL assay (green). Apoptotic RGCs were observed in the MCAO+vehicle group, while
KIOM-2015E application reduced retinal tissue damage. Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive cells in the GCL. All images
were acquired at 40× magnification. Scale bar: 100 μm. Data are presented as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). ***p<0.001
versus sham-operated, # p<0.05, ## p<0.01, ### p<0.001 versus MCAO+vehicle (E.D.). MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion;
RGC, retinal ganglion cell; G.F., Ginexin F; GCL, ganglion cell layer; TUNEL: terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end
labeling.
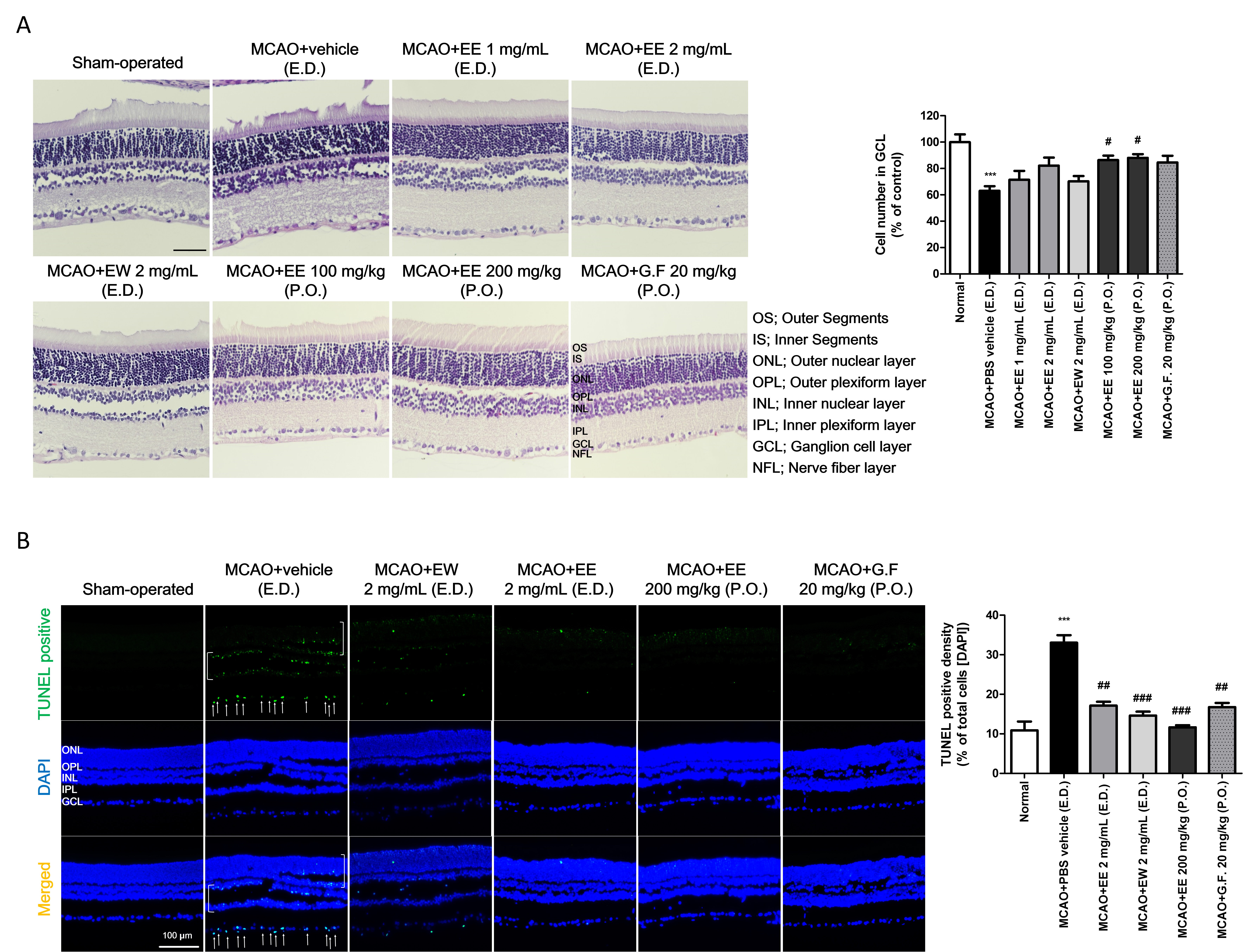
 Figure 3 of
Kim, Mol Vis 2020; 26:691-704.
Figure 3 of
Kim, Mol Vis 2020; 26:691-704.  Figure 3 of
Kim, Mol Vis 2020; 26:691-704.
Figure 3 of
Kim, Mol Vis 2020; 26:691-704. 