Figure 2. The application of KIOM-2015E for 5 days after MCAO inhibits the activation of Müller cells and astrocytes. SD rats were treated
using topical eye drops (E.D., three times daily) or via oral administration (P.O., once daily) of KIOM-2015EW, KIOM-2015EE,
or Ginexin-F. Five days after treatment, activation of Müller cells and astrocytes was determined by immunofluorescent staining
of retinal flat mounts with antibodies against glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; a marker of Müller and astrocytes; A) and by immunofluorescent staining of retinal tissue—which was paraffin-embedded and vertically sectioned—with an antibody
against glutamine synthase (GS; a marker of astrocytes; B). Strong activation of GFAP and GS was observed in the MCAO+vehicle group relative to that observed in the sham-operated
group. However, treatment with KIOM-2015E inhibited the activation of Müller cells and astrocytes. Quantitative analysis of
fluorescence density in GFAP-stained flat-mounted and GS-stained vertically sectioned retinal tissues. Five pictures were
randomly selected per group. The average fluorescence density was calculated using the ImageJ program and expressed as a percentage
of the value for the sham-operated group. All images were acquired at 40× magnification. Scale bar: 200 μm. Data are presented
as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). ***p<0.001 versus sham-operated, ###p<0.001 versus MCAO+vehicle (E.D.). MCAO,
middle cerebral artery occlusion; RGC, retinal ganglion cell; G.F., Ginexin F; GCL, ganglion cell layer.
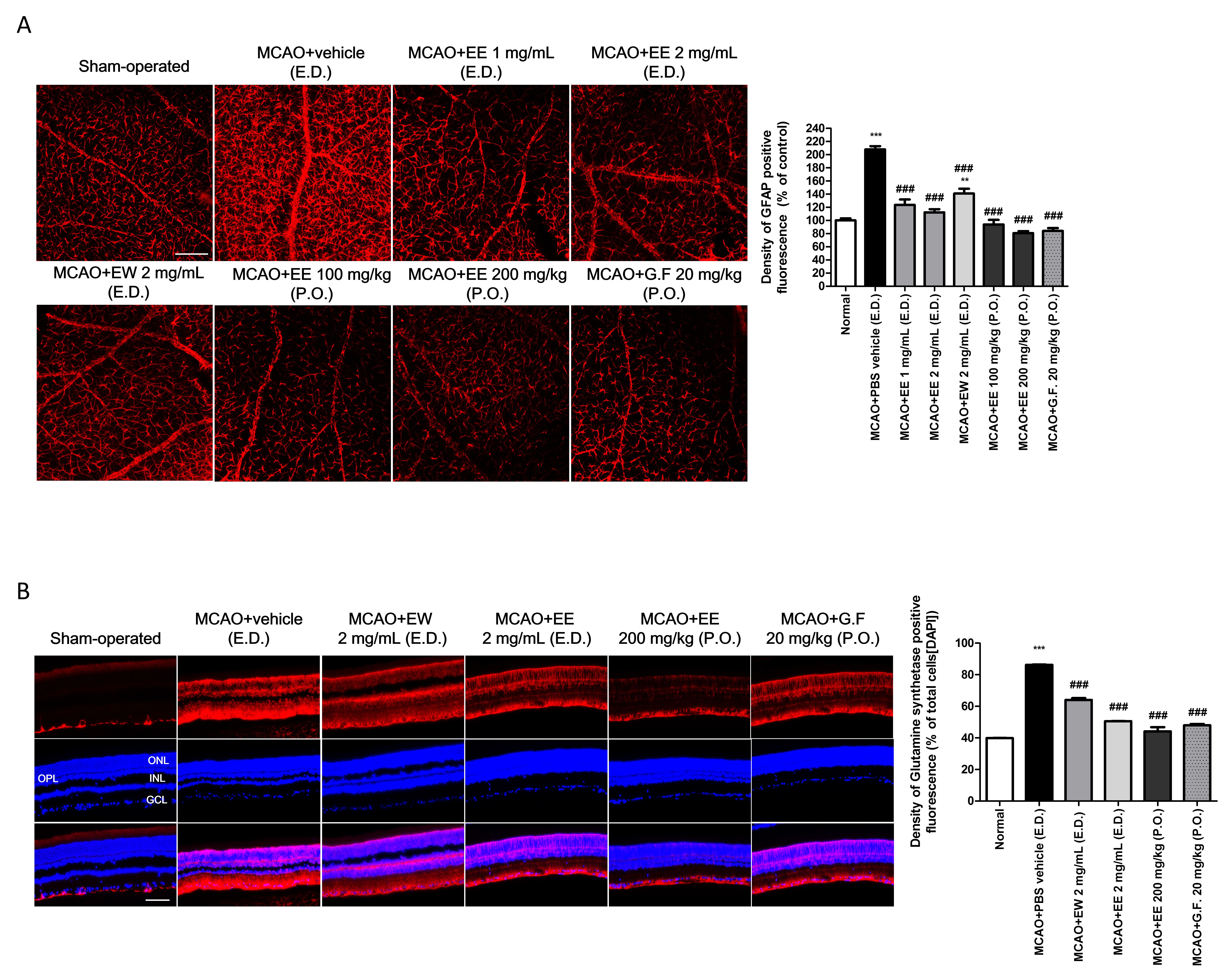
 Figure 2 of
Kim, Mol Vis 2020; 26:691-704.
Figure 2 of
Kim, Mol Vis 2020; 26:691-704.  Figure 2 of
Kim, Mol Vis 2020; 26:691-704.
Figure 2 of
Kim, Mol Vis 2020; 26:691-704. 