Figure 4. Location and structure of the D144G missense mutation. A: Sequence chromatograms of the detected mutations in GUCA1A. The top chromatogram represents the sequence of a healthy family member (III:5). The middle (III:2) and bottom (IV:3) chromatograms
show a missense mutant sequence, which is A–G transversion in exon 5 of GUCA1A. The arrow indicates the location of the mutation. B: Orthologous protein sequence alignment of GCAP1 from multiple species. The 144 GLY of the EF4 loop region replaced the negatively
charged ASP residue (arrows). Conservative residues are printed on a black background. The 12-amino-acid loop of the EF4-hand
domains of the protein are underlined, and the other six known mutations are indicated with an asterisk. C: The structure
of the GCAP1 three-dimensional homologous model. EF1 is slate, EF2 is yellow, EF3 is green, and EF4 is orange. The N- and
C-terminal helixes are gray white and pale cyan, while the loop is deep pink. Mutated amino acids are indicated in red, and
Ca2+ ions are shown as red spheres. Residue D144 is shown as sticks, and 144 GLY is magenta and also shown as sticks. P50L is
located in the EF1-EF2 link; Y99C, D100E, and E111V are located in EF3; and E155G, G159V, and D144G are located in EF4. D: Details of the region surrounding D144G. Hydrophobic residues showing persistent interactions with D144G are labeled as
sticks. The hydrogen bonds are highlighted in green. The hydrogen bonds between residue 144 and residue Phe140 or Gly147 were
eliminated upon changing from the wild-type ASP to mutant GLY.
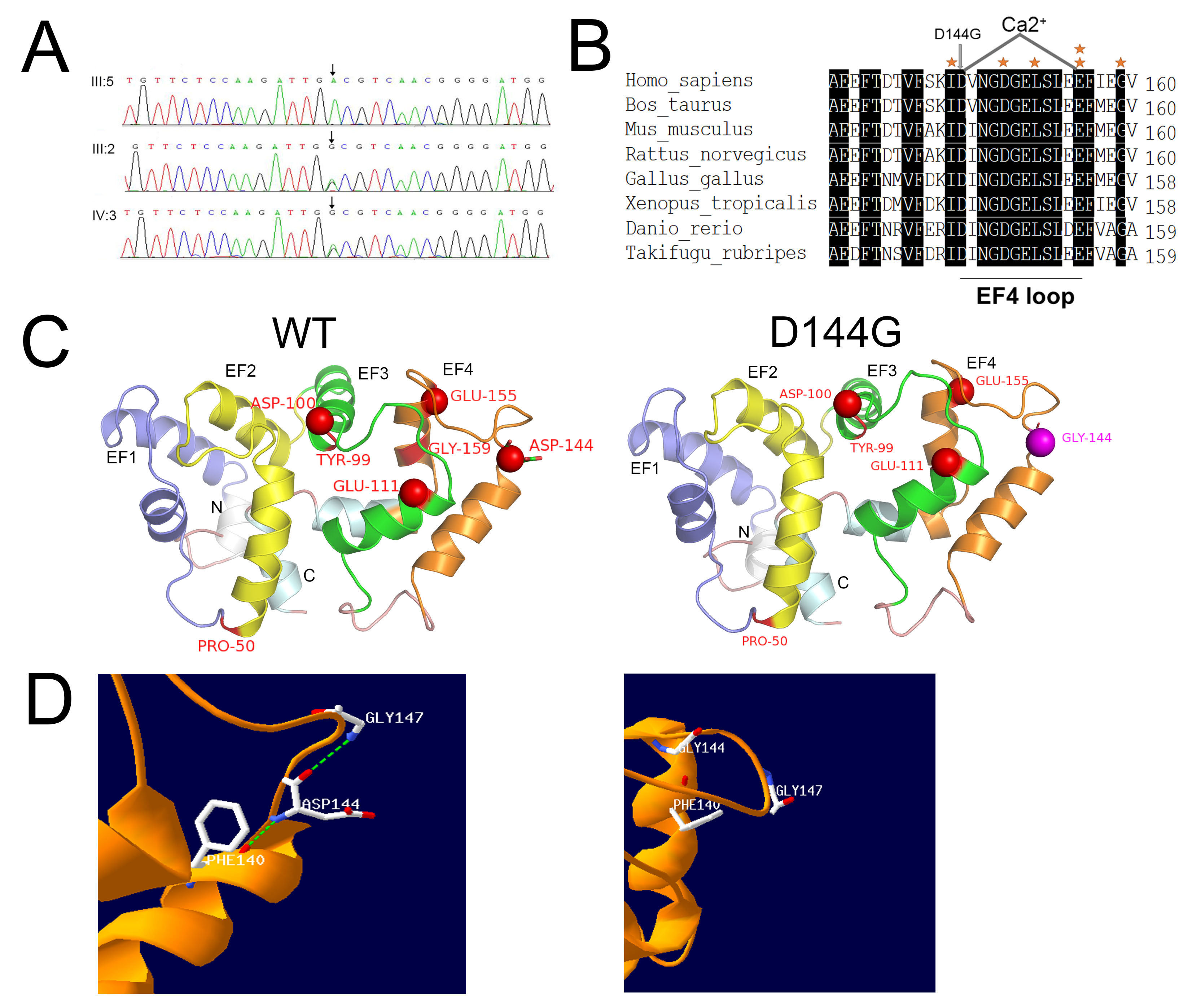
 Figure 4 of
Tang, Mol Vis 2019; 25:921-933.
Figure 4 of
Tang, Mol Vis 2019; 25:921-933.  Figure 4 of
Tang, Mol Vis 2019; 25:921-933.
Figure 4 of
Tang, Mol Vis 2019; 25:921-933. 