Figure 5. GREM1 knockdown alleviated EMT and promoted redifferentiation in high passage fetal RPE cells by enhancing the BMP pathway. A: The quantitative PCR (qPCR) results show that the GREM1 knockdown makes GREM1 downregulate efficiently. B: On day 4 after transfection, some siGREM1 group cells appear to have a relatively normal cobblestone-like shape compared to the NC group cells and an appearance less
like epithelium-mesenchymal transition (EMT). C: The qPCR results show that after transfection, SNAI1 had no statistically significant difference, but VIM is reduced, and the RPE-related genes, such as MITF, OTX2, and RPE65 are upregulated in the siGREM1 group cells compared to the NC group cells. D: The western blotting results show that in the siGREM1 group cells, ZO-1 and p-Smad1 are increased, but vimentin is decreased compared to the NC group cells. However, p-Smad2 has
no statistically significant differences between the two groups. Actin serves as an internal reference in the western blots.
Scale bar: 100 μm. Data are shown as the mean ± standard error of mean (SEM), n=3, **p<0.01 *p<0.05 versus NC groups. Ph:
Phase contrast micrograph; siGREM1: GREM1 knockdown by siRNA group; NC group: Negative group. p-Smad2: phosphorylated-Smad2; p-Smad1: phosphorylated-Smad1.
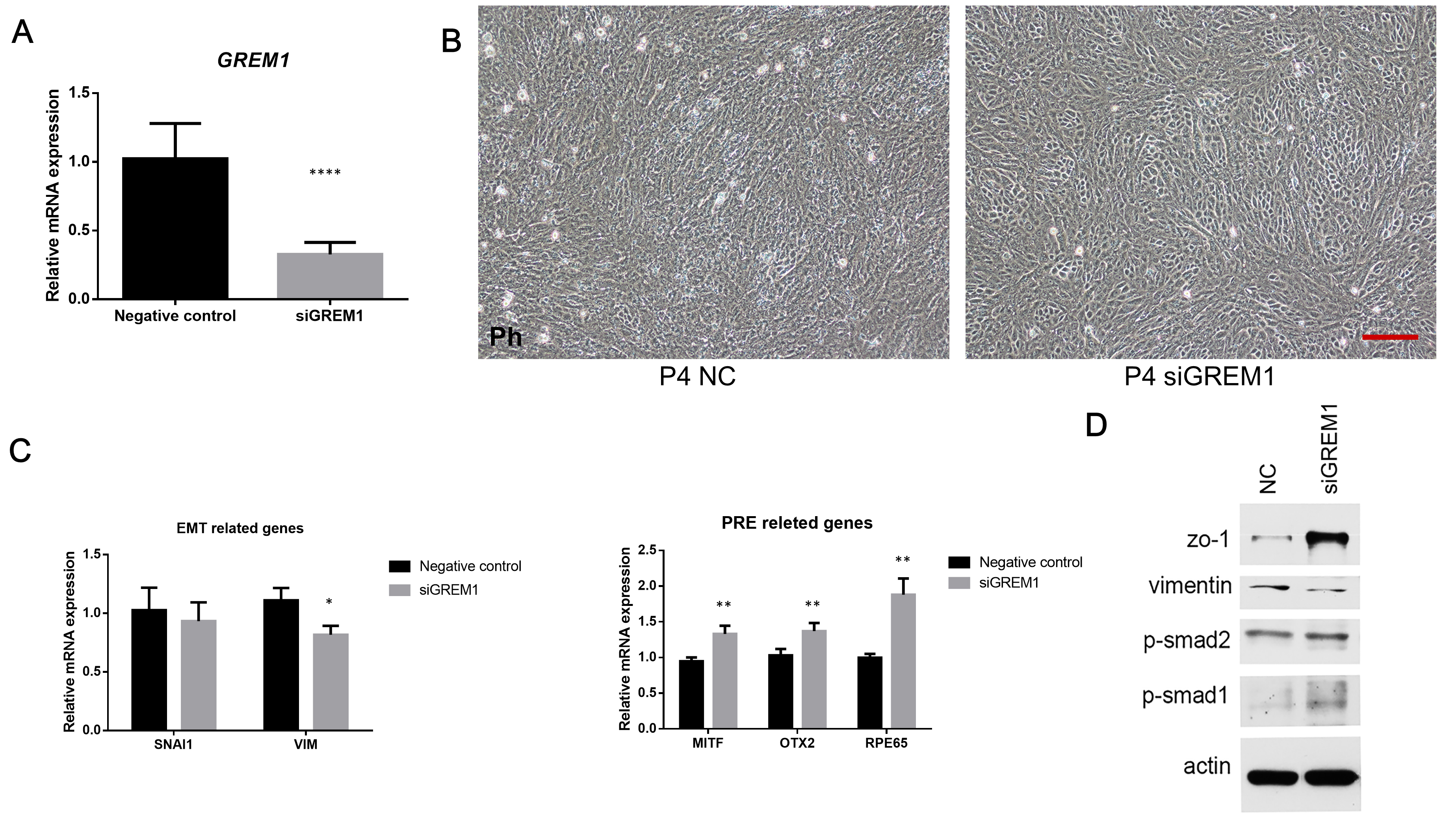
 Figure 5 of
Li, Mol Vis 2019; 25:625-635.
Figure 5 of
Li, Mol Vis 2019; 25:625-635.  Figure 5 of
Li, Mol Vis 2019; 25:625-635.
Figure 5 of
Li, Mol Vis 2019; 25:625-635. 