Figure 1. Schematic representation of synthesis and circulation of bile acids. Primary bile acids (BAs), cholic acid (CA), and chenodeoxycholic
acid (CDCA) are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol and stored in the gallbladder. Following food intake, bile acids
are released into the small intestine. Secondary bile acids are produced by the gut microbiota from modifications of primary
bile acids. Deoxycholic acid (DCA) is formed from CA. Lithocholic acid (LCA) and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) are formed by
CDCA. Taurine conjugation of UDCA forms tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA). About 95% of the bile acids are reabsorbed in the
ileum, and 5% are lost in feces. The bile acids absorbed by the enterocytes are released into the portal vein and redirected
to the liver for recycling (enterohepatic circulation). Only a small portion (10%) escapes the enterohepatic circulation and
reaches the systemic circulation.
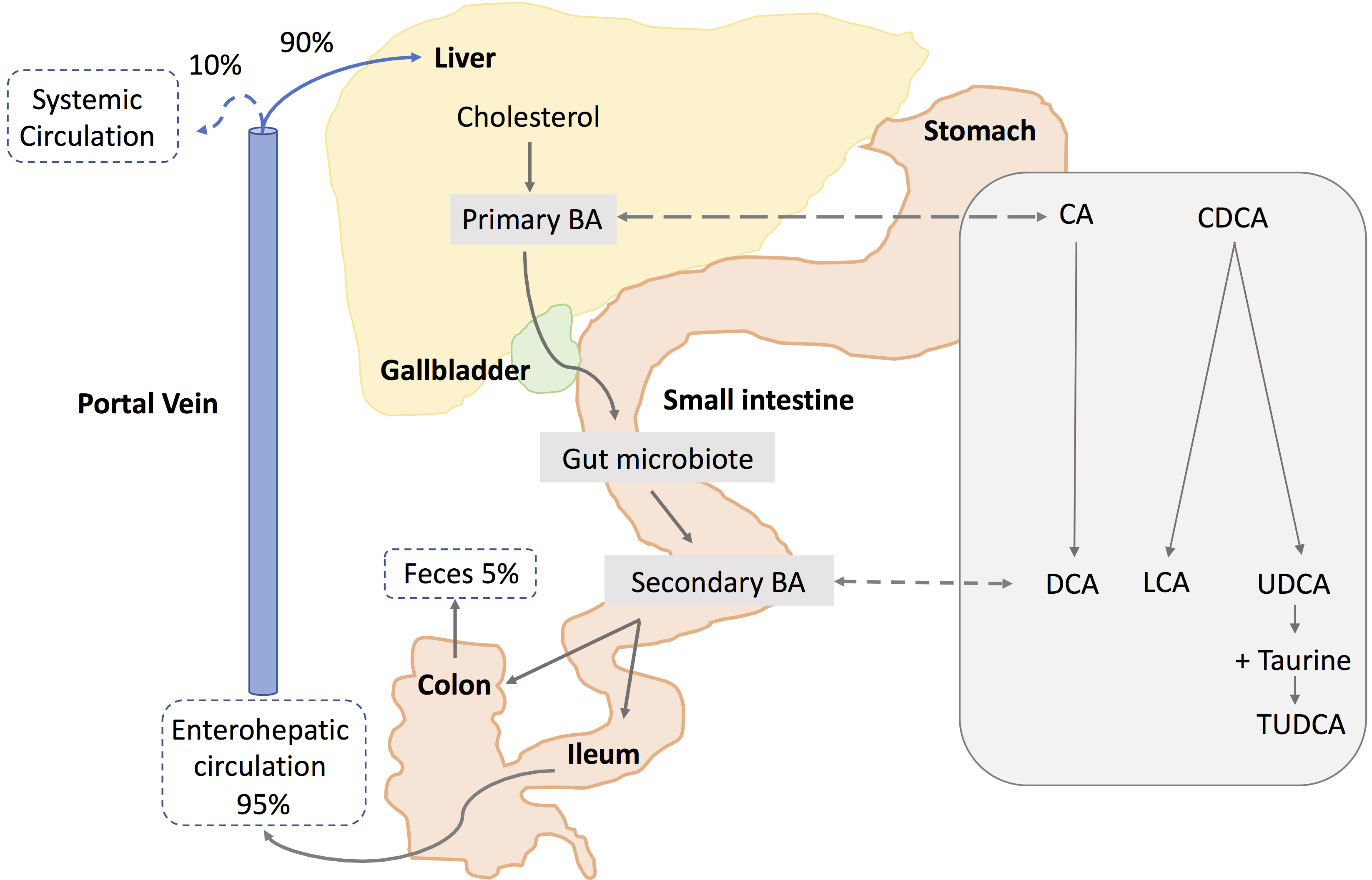
 Figure 1 of
Daruich, Mol Vis 2019; 25:610-624.
Figure 1 of
Daruich, Mol Vis 2019; 25:610-624.  Figure 1 of
Daruich, Mol Vis 2019; 25:610-624.
Figure 1 of
Daruich, Mol Vis 2019; 25:610-624. 