Figure 5. Signaling pathways involved in thrombin-induced glutamate release. A: Protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1)-induced glutamate (Glu) release requires phospholipase C-β (PLC-β) activity. Cells
were incubated in the presence of the PLC-β inhibitor U73122 (2.5 μM) for 30 min. The inhibitor was removed before stimulation
with 10 μM PAR-1 AP. Results showed that Ser-Phe-Leu-Leu-Arg-Asn-amide trifluoroacetate salt (SFLLRN) induced Glu release
which was prevented by the inhibition of PLC-β. Results are the mean of three independent experiments. The Student t test with respect to negative control was statistically significant (*p<0.05). The Student t test with respect to SFLLRN was statistically significant (@ p<0.05). B: Inhibition of c/n protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms prevents SFLLRN-induced Glu release. Cells were incubated with the c/n
PKC inhibitor Ro 32–0432 (20μM) for 30 min, and removed before stimulation with 10 μM PAR-1 AP. Data are the mean ± standard
error of the mean (SEM) of three independent experiments. The Student t test with respect to negative control was statistically significant (**p<0.005). The Student t test with respect to SFLLRN was statistically significant (@ p<0.05). C: Thrombin-induced Glu release is independent of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
(MEK) activity. The MEK inhibitor U0126 (20 μM) and the PI3K inhibitor wortmannin (1 μM) were included in KRB for 30 min and
removed, before stimulation. Data are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. The Student t test with respect to negative control was statistically significant (**p<0.005). The Student t test with respect to SFLLRN was not statistically significant.
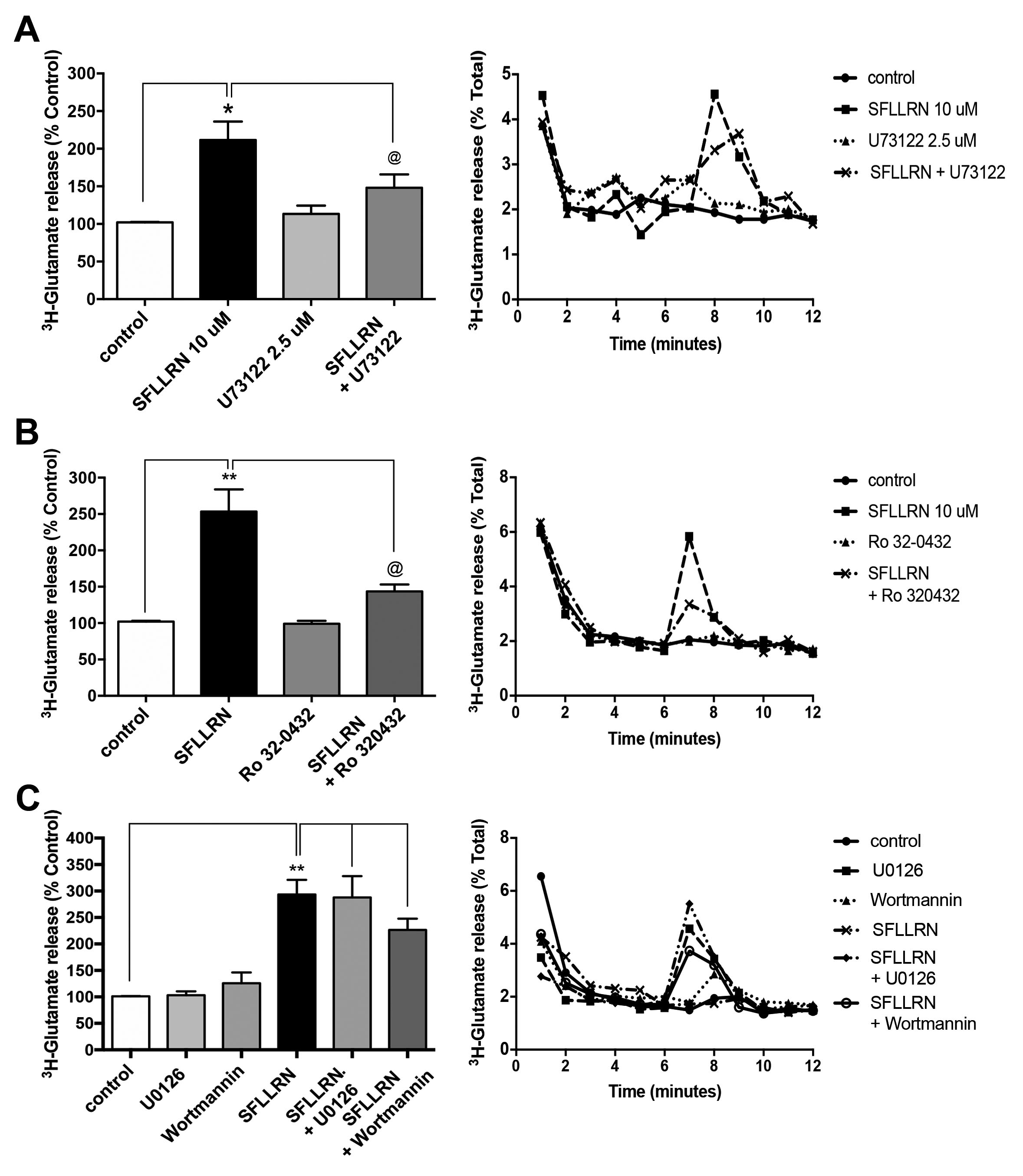
 Figure 5 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558.
Figure 5 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558.  Figure 5 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558.
Figure 5 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558. 