Figure 4. SFLLRN-induced glutamate release is calcium-dependent. Primary cultures of rat RPE cells loaded with 1 µCi/ml 3H-glutamate in Krebs ringer bicarbonate (KRB) for 30 min and stimulated with 10 μM protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1) AP
(Ser-Phe-Leu-Leu-Arg-Asn-amide trifluoroacetate salt [SFLLRN]). A: SFLLRN-induced glutamate release is calcium-dependent. 1,2-Bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid tetrakis(acetoxymethyl
ester) (BAPTA AM) and/or EGTA were included in Ca2+-free KRB for 15 min in the presence or absence of the Ca2+ chelators BAPTA-AM (10 μM) and/or EGTA (1 mM) before stimulation. Values are the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM)
of three independent experiments. The Student t test with respect to negative control was statistically significant (**p<0.005); the Student t test with respect to SFLLRN w/ Ca2+ was statistically significant (@@p<0.005); the Student t test with respect to SFLLRN w/o Ca2+ was statistically significant (#p<0.05, ##p<0.005). B: Ca2+ release from intracellular stores is the main contributor to PAR-1 induced glutamate release. Cells were stimulated with
5 μM ionomycin to further demonstrate the requirement for intracellular Ca2+. Values are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. The Student t test with respect to negative control was statistically significant (*p<0.05). C: Extracellular Ca2+ contributes to PAR-1-induced glutamate release. Cells were incubated with the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) inhibitor SEA 0400 (50 μM), and of the inhibitor of the exchanger reverse activity KB-R7943 (75 μM) before
stimulation with 10 μM of the PAR-1 agonist peptide SFLLRN. Results showed that PAR-1-induced release was statistically significantly
decreased by these compounds. Data are the mean of three independent experiments. The Student t test with respect to negative control was statistically significant (**p<0.005); the Student t test with respect to SFLLRN was statistically significant (@@p<0.005). D: PAR-1-induced glutamate release is independent of L-type calcium channel activation. Thrombin stimulation in the presence
of the L-type calcium channel blocker nifedipine (5 μM) showed that Glu release is unrelated to L-calcium channel activity.
Values are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. The Student t test with respect to negative control was statistically significant (***p<0.005). The Student t test with respect to SFLLRN was not statistically significant.
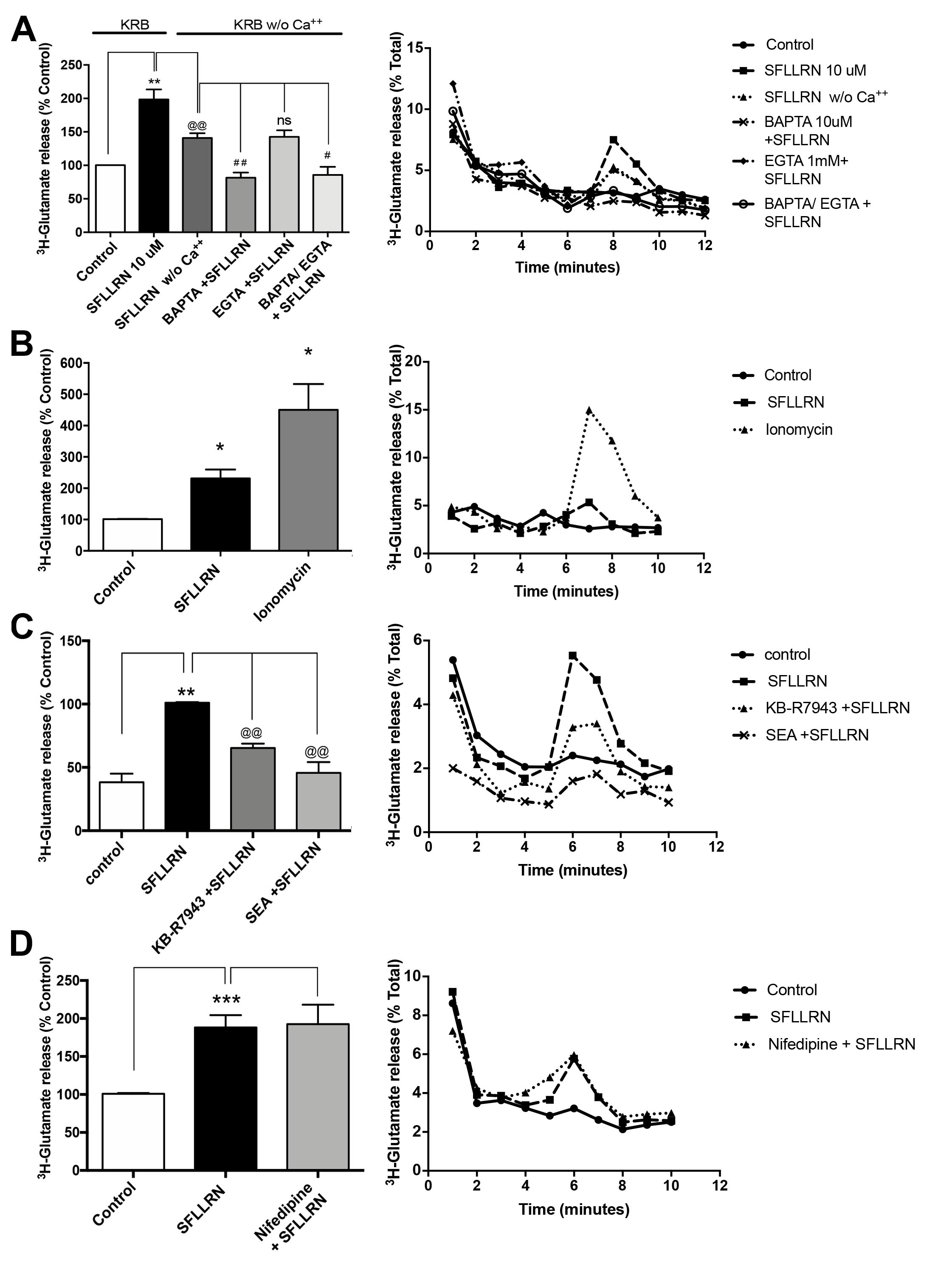
 Figure 4 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558.
Figure 4 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558.  Figure 4 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558.
Figure 4 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558. 