Figure 2. Thrombin induces glutamate release from rat RPE cells. Primary cultures of rat RPE cells were incubated for 30 min with 1
mM amino-oxyacetic acid and 0.5 mM methionine sulfoximine (AAOA-MSO) before loading with 3H-glutamate in Krebs ringer bicarbonate (KRB; 1 µCi/ml 30 min). Cultures were superfused with KRB containing 50 μM 1-transpyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic
acid (trans-PDC) and stimulated with 2 U/ml thrombin. One milliliter samples were collected at 1 min intervals. Results are
expressed as % of total 3H-Glu incorporation or as a % of unstimulated control. A: Thrombin stimulates glutamate release. Thrombin-induced 3H-Glu release was increased by the inhibition of glutamate (Glu) metabolism and reuptake. Values are the mean ± standard error
of the mean (SEM) of three independent experiments. The Student t test with respect to negative control was statistically significant (*p<0.05; ** p<0.005). B: Specificity of the thrombin effect. Thrombin-induced Glu release was prevented by the inclusion of thrombin inhibitors hirudin
(4 U/ml) and D-Phenylalanyl-Prolyl-Arginyl Chloromethyl Ketone (PPACK; 10 μM) during superfusion. Values are the mean ± SEM
of three independent experiments. The Student t test with respect to negative control was statistically significant (**p<0.005); the Student t test with respect to thrombin stimulation was statistically significant (@p<0.05; @@p<0.005).
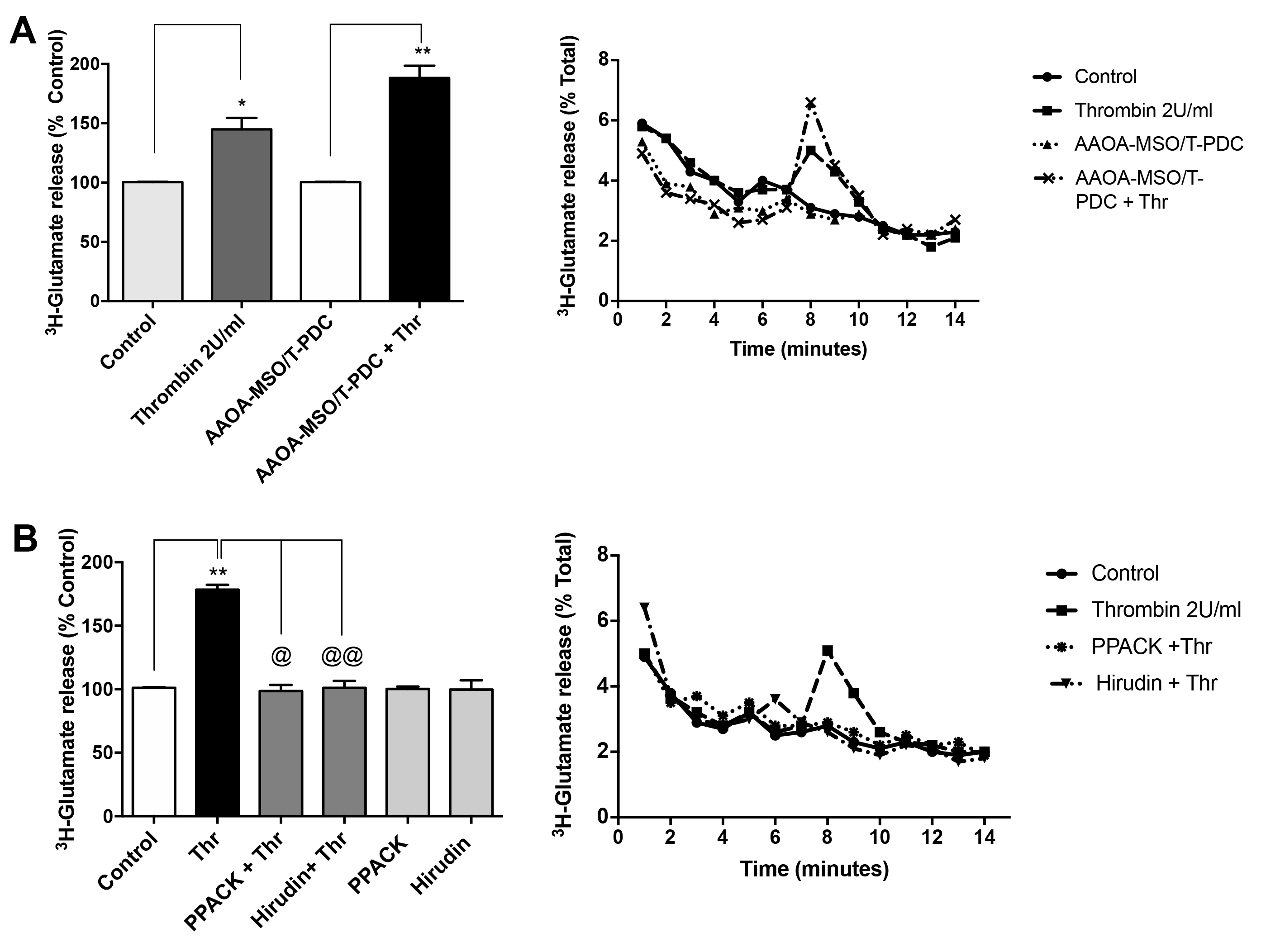
 Figure 2 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558.
Figure 2 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558.  Figure 2 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558.
Figure 2 of
López, Mol Vis 2019; 25:546-558. 