Figure 2. Ex vivo assessment of the effect of antioxidant treatments on hMDM neurotoxicity. Mouse retinal explants were incubated for
18 h with M1 (A, n=7) or M2a (B, n=8) human monocyte-derived macrophages (hMDMs) which were supplemented with the four antioxidant treatments (G1–G4). Un-supplemented
media served as control (G5). The apoptosis level was evaluated using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end
labeling (TUNEL) labeling under a confocal microscope. No treatments affected the toxicity level of the M1 hMDMs compared
to that of the control group. However, treatment with G2, G3, and G4 reduced the toxicity of the M1 hMDMs compared to treatment
with G1 (repeated-measure mixed-effect model, +p≤0.05 compared to G1 (A)). The M2a hMDMs supplemented with the G2 and G4 treatments were associated with an increasing toxicity level compared to
that of the control group and the G3 treatment group (*p≤0.05 compared with control and $p≤0.05 compared to G3 (B)). For apoptosis quantification, the entire retina was stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-nuclei labeling
(blue; C) and TUNEL labeling (red; D), and then merged (E). Eleven fields were automatically chosen around the optic nerve, magnified at 40X (F). Photos from each field were split into blue and red channels (G, H), and then converted into 8-bit images (I), which underwent water sheet processing to delineate each cell (J). The total numbers of cells were then automatically quantified, and the numbers of apoptotic cells were calculated as the
percentage of the total number of cells stained with DAPI (K).
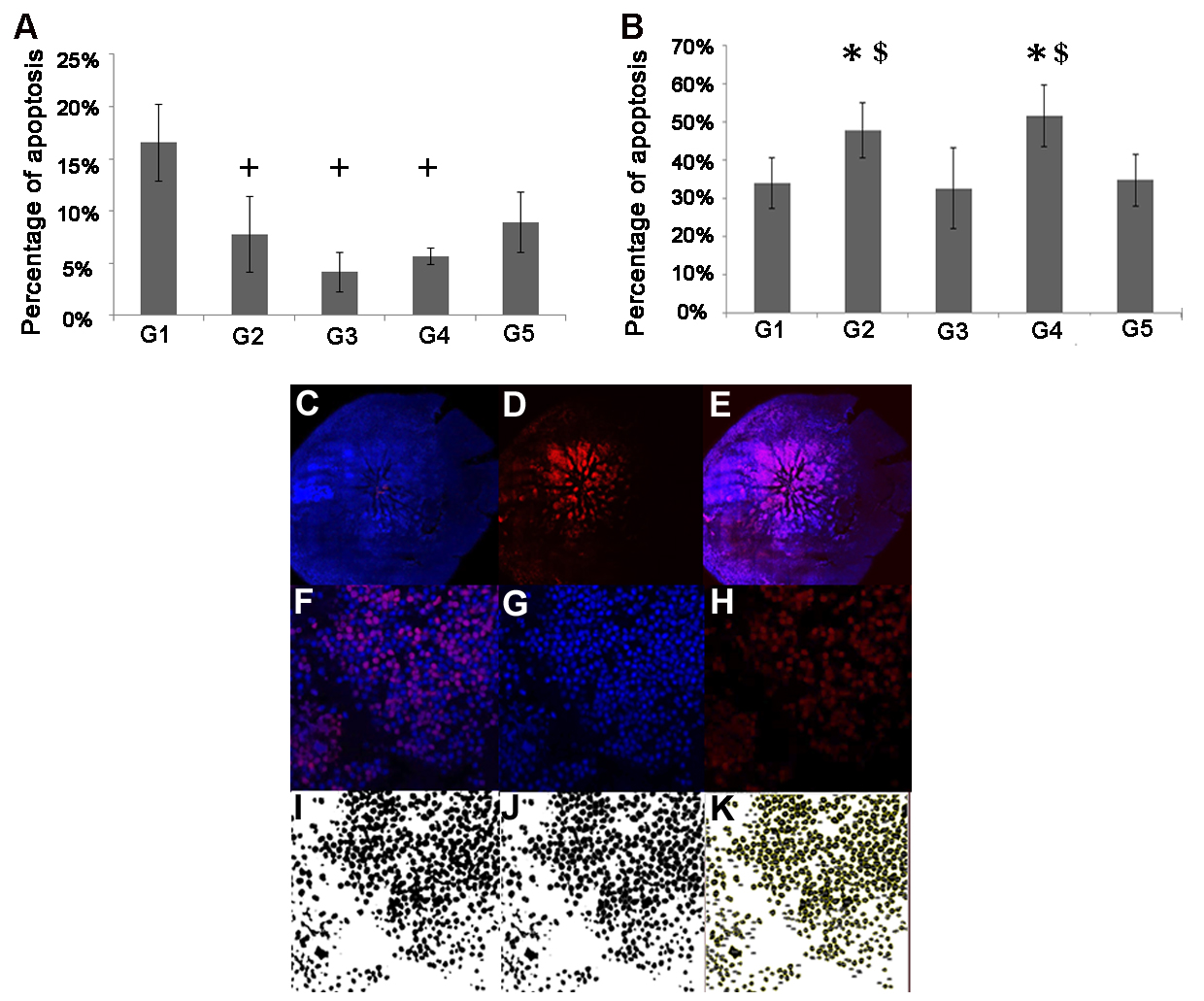
 Figure 2 of
Elbaz-Hayoun, Mol Vis 2019; 25:479-488.
Figure 2 of
Elbaz-Hayoun, Mol Vis 2019; 25:479-488.  Figure 2 of
Elbaz-Hayoun, Mol Vis 2019; 25:479-488.
Figure 2 of
Elbaz-Hayoun, Mol Vis 2019; 25:479-488. 