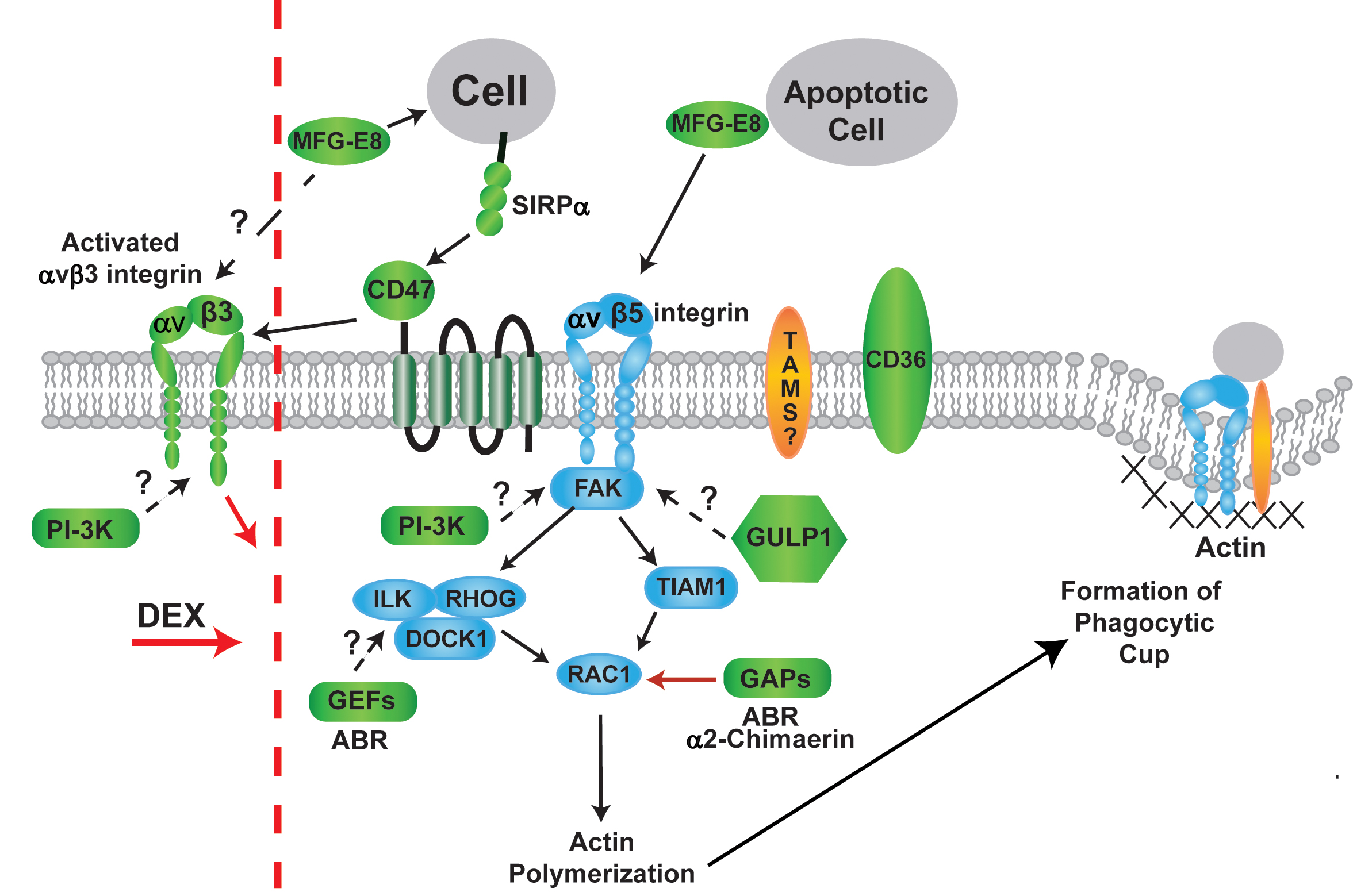
Figure 1. αvβ5 integrin/FAK-mediated phagocytic pathway in TM-1 cells. The diagram illustrates the αvβ5 integrin/FAK signaling pathway
used by TM cells to control RAC1 activity in phagocytosis. Proteins shown to be previously involved are indicated in blue
and suggest that two separate pathways, one involving the GEF Tiam1 and the other involving a ILK/RHOG/ELMO2 complex, appear
to be used by TM-1 cells to activate RAC1 [
12]. In other cells, the activation of RAC1 leads to the polymerization of actin filaments to form the phagocytic cup and the
engulfment of cellular debris (unlabeled gray circle) attached to αvβ5 integrin and a member of the TAM family, such as MerTK
[
56]. Whether MerTK is involved in TM cell phagocytosis is not known. Proteins identified in this proteomic study and their possible
involvement in the pathway are in green. How PI-3K is involved in phagocytosis is unknown. One possible role is via interactions
with the αvβ5 integrin/FAK signaling pathway. The red dotted line indicates that prior studies have shown that treatment with
DEX and/or activation of αvβ3 integrin inhibits phagocytosis in these cells [
11]. Although it is not known how αvβ3 integrin is activated by DEX, interactions with MFG-E8 or CD47, which does activate αvβ3
integrin, could be involved. The red arrows indicate an inhibitory role. Dashed arrows and question marks indicate a possible
interaction.
 Figure 1 of
Faralli, Mol Vis 2019; 25:237-254.
Figure 1 of
Faralli, Mol Vis 2019; 25:237-254.  Figure 1 of
Faralli, Mol Vis 2019; 25:237-254.
Figure 1 of
Faralli, Mol Vis 2019; 25:237-254.