Figure 5. Inhibition of FGF2 signaling blocks the RCM formation induced by surgical injury in the mouse corneal endothelium in vivo.
A: The uninjured control cornea showed a well-organized monolayer of corneal endothelial cells. B: At 14 weeks after surgical injury, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining showed an extensive retrocorneal membrane (RCM)
with thickening and disorganization of Descemet’s membrane in the injured cornea (arrowhead). C: fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) siRNA knockdown completely blocked RCM formation induced by surgical injury. FGF2 siRNA
knockdown also left a persistent defect in Descemet’s membrane and the endothelium 14 weeks after injury. Scale bar, 50 µm.
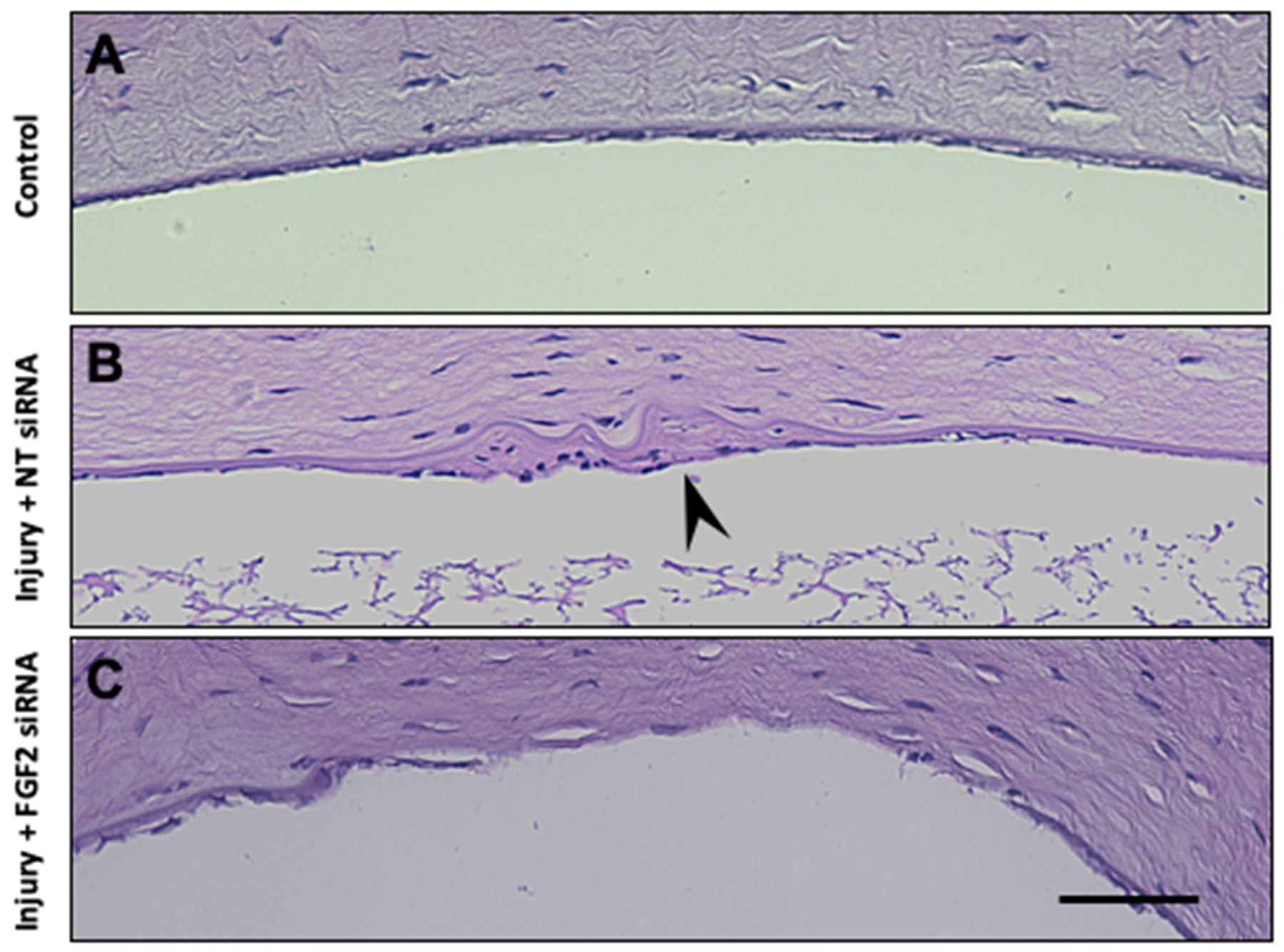
 Figure 5 of
Lee, Mol Vis 2019; 25:22-34.
Figure 5 of
Lee, Mol Vis 2019; 25:22-34.  Figure 5 of
Lee, Mol Vis 2019; 25:22-34.
Figure 5 of
Lee, Mol Vis 2019; 25:22-34. 