Figure 1. Osmolarity-dependent expression of complement factor genes in cultured human RPE cells. mRNA levels were determined with real-time
RT–PCR analysis. A: Presence of complement gene transcripts in RPE cells. To confirm the correct lengths of PCR products, agarose gel electrophoresis
was performed using products obtained from freshly isolated human RPE cells of two different post-mortem donors (f1, f2) and
from cultured human RPE cells of the 5th (c1) and 4th (c2) passage, respectively. Negative controls (0) were obtained by using
double-distilled water instead of cDNA as a template. GAPDH mRNA was used as a loading control. B: Relative expression levels of complement genes in cells cultured for 2 h, 6 h, and 24 h (as indicated by the panels of the
bars) in hyperosmotic medium (+ 100 mM NaCl). C: Dose-dependent effect of high extracellular NaCl on the C9 mRNA level. Extracellular hyperosmolarity was induced by the
addition of 10–100 mM NaCl to the culture medium. D: Effects of hyperosmotic (+ 100 mM sucrose) and hypoosmotic (Hypo; 60% osmolarity) media on the expression of the C9 gene.
The numbers of independent experiments using cell lines from different donors are indicated in or above the bars. Significant
difference versus isosmotic control: *p<0.05.
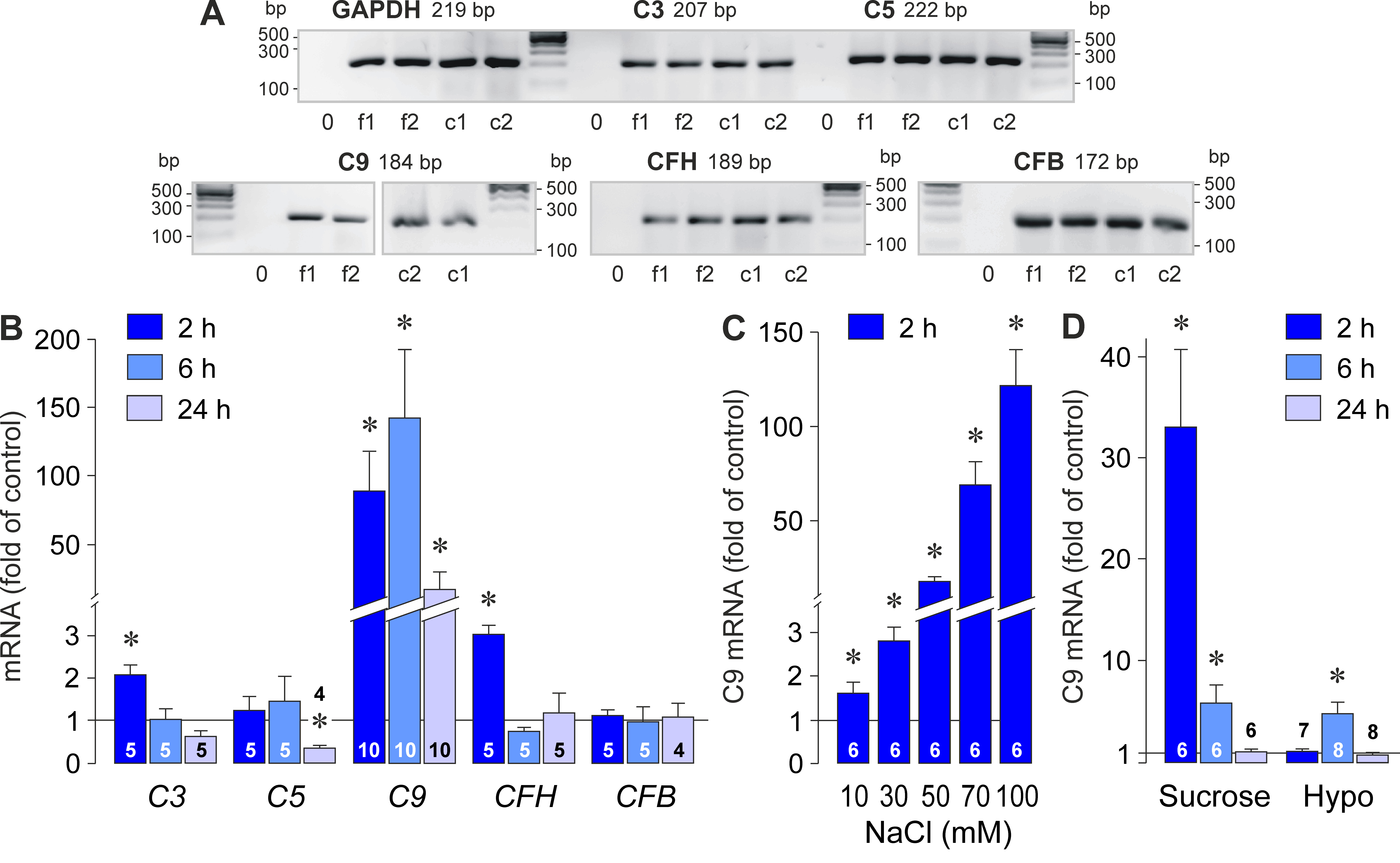
 Figure 1 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2018; 24:518-535.
Figure 1 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2018; 24:518-535.  Figure 1 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2018; 24:518-535.
Figure 1 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2018; 24:518-535. 