Figure 7. FPR2 mediated the RvD1-induced promotion of regeneration of the corneal epithelium in diabetic mice. These experiments were
performed in diabetic, resolvin D1 (RvD1) treated, and RvD1 plus WRW4-treated diabetic mice. A: The residual epithelial defect was examined at 0, 24, and 48 h after the removal of the corneal epithelium with fluorescein
staining as described previously. B: The histogram of the residual epithelium defect is presented as the percentage of the original wound area (n=6). C: The accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the synthesis of glutathione (GSH) were tested with immunofluorescence
staining at 48 h after removal of the epithelium. D: The western blotting results show the expression level of antioxidants, including MnSOD, NQO-1, and HO-1, 48 h after the
removal of the epithelium. E: The quantified data of western blotting results are shown (n=4). Data are given as the mean ± standard deviation (SD); *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
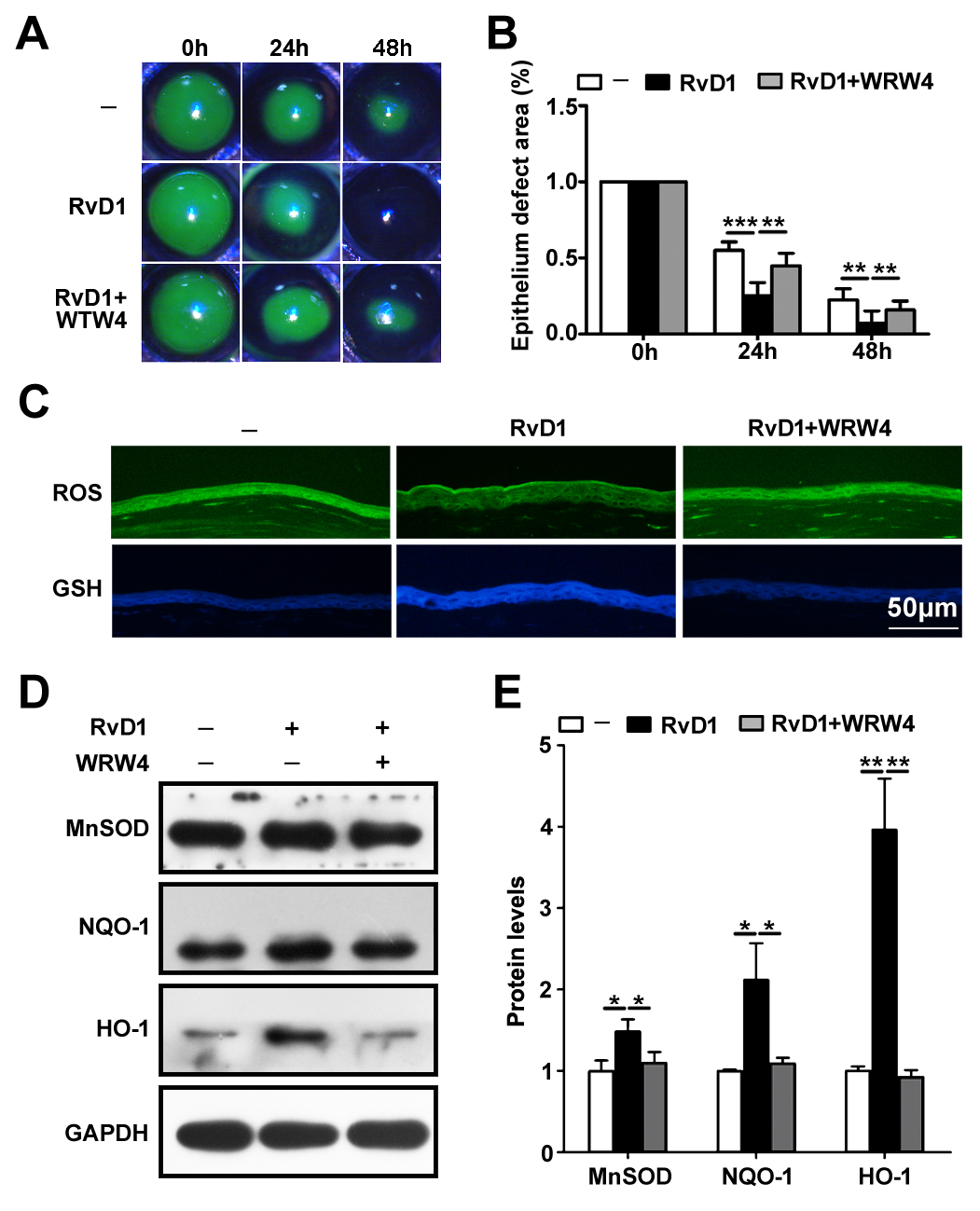
 Figure 7 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2018; 24:274-285.
Figure 7 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2018; 24:274-285.  Figure 7 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2018; 24:274-285.
Figure 7 of
Zhang, Mol Vis 2018; 24:274-285. 