Figure 2. Comparison between the structure and solubility of WT and MU-βB1 proteins. A: Diagrammatic sketch of βB1 protein features. The hollow triangle indicates the position of p.Q227X; the hollow rectangle
indicates the truncated partial motif VI and C-terminus. B: Multiple-sequence alignment of βB1-crystallin. The Gln227 residue is highly conserved during evolution shown with a solid
triangle. C: The predicted tertiary structure of wild-type (WT) βB1-crystallin. D: The predicted tertiary structure of mutated βB1-crystallin. The C-terminus of the wild-type protein is pointed by an arrow,
which disappeared in the mutant. E: Distribution of the recombinant expression of the WT and mutant (MU) βB1 proteins in the Escherichia coli (DE3) strain. I = inclusion bodies; S = supernatant; the arrow indicates the WT or MU βB1 proteins. F: Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) analysis of purified WT-βB1, its truncation mutant
(MU-βB1), and αA-crystallin. Lanes: WT, WT-βB1; MU, MU-βB1; αA, αA-crystallin.
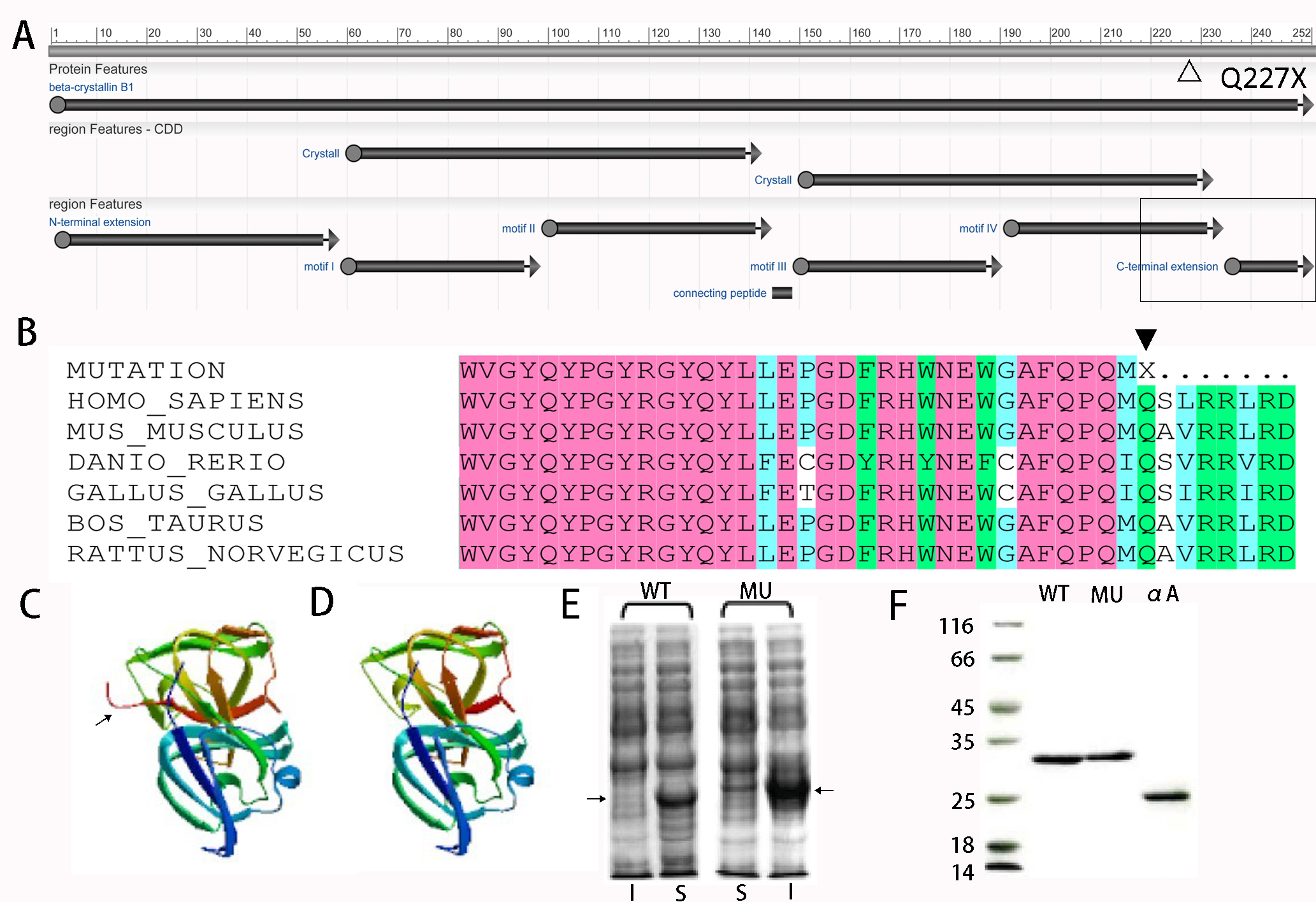
 Figure 2 of
Rao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:624-637.
Figure 2 of
Rao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:624-637.  Figure 2 of
Rao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:624-637.
Figure 2 of
Rao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:624-637. 