Figure 1. Mutation analysis of CRYBB1 in a Chinese family with congenital cataract. A: Pedigree and haplotype analysis of the family showing the segregation of six microsatellite markers on chromosome 22q11.2–12.1.
Squares and circles indicate men and women, respectively. Solid symbols and bars denote affected status. The proband is indicated
with an arrow. C/C and C/T indicate the CRYBB1 genotypes. B: Front view of the eye of the proband, showing dense nuclear opacities with nystagmus. C: Slit-lamp view of the lens of the proband. Lens opacities are mainly located in the nuclear area of the lenses, as well
as in the embryonal and fetal areas. D, E: Sequence chromatograms of one unaffected individual (D) and one affected individual (E) of exon 6 of the CRYBB1 gene in this family with autosomal dominant congenital cataract (ADCC). The DNA sequence chromatogram shows a c. 749 C>T
heterozygous mutation in CRYBB1 indicated by an arrow in panel E.
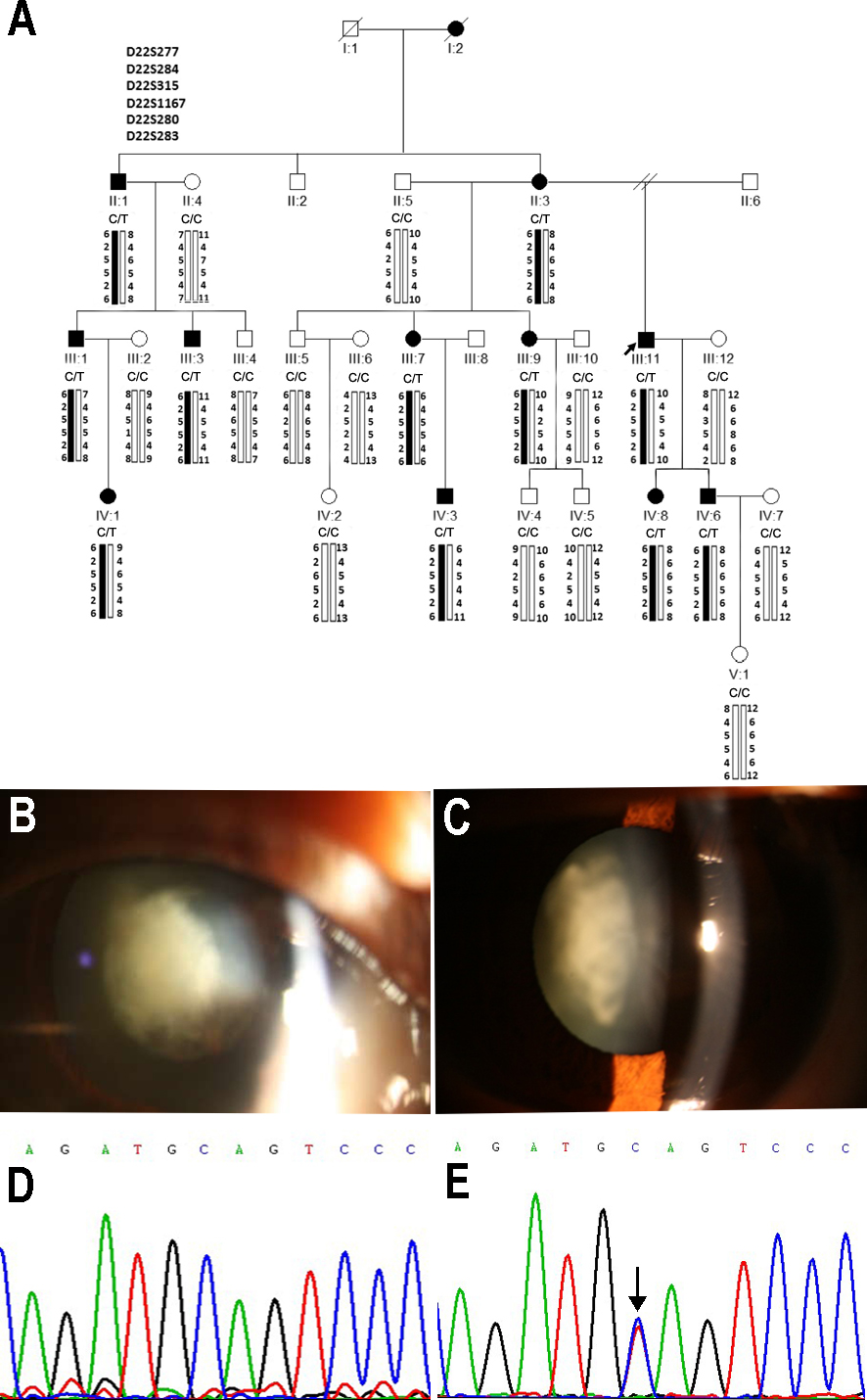
 Figure 1 of
Rao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:624-637.
Figure 1 of
Rao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:624-637.  Figure 1 of
Rao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:624-637.
Figure 1 of
Rao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:624-637. 