Figure 2. Pedigree drawing of family E showing autosomal recessive inheritance. A: The red arrow indicates the affected individual for whom whole exome sequencing (WES) was performed. B: Affected individual IV-3 has typical features of BBS syndrome, including hypertelorism, deep-set eyes, a flat nasal bridge,
a small mouth, retrognathia, malar hypoplasia, and curly hair. C, D: Dorsal and palmar view of hands that have postaxial polydactyly only in the left hand. E: Feet of affected individual IV-3 who has obesity and bilateral post axial polydactyly. F: Typical BBS facial features shown in affected individual IV-4: flat nasal bridge, poor eyesight, intellectual disability,
and a small mouth. G, H: Dorsal and palmar view of the hands (IV-4) and postaxial polydactyly in the right hand. I: Feet of affected individual IV-4, showing obesity but no polydactyly. J: The gene structure of the MKKS gene. The arrow shows the mutation (c.119C>G) identified in exon 1 of the MKKS gene in the present study. K: Schematic representation of the MKKS protein domains (equatorial, intermediate, and apical domain); the red arrow shows
the identified mutation (p.Ser40*) within the MKKS equatorial domain. Intronic regions are not drawn to scale. L: The upper panel shows the nucleotide sequence in the homozygous affected individual. M: The middle panel shows the nucleotide sequence in the heterozygous carrier. N: The lower panel shows the nucleotide sequence in the homozygous normal individual in each sequence chromatogram. O: Partial amino acid sequence comparison of the human MKKS protein with other orthologs showing serine residue in green conserved
across different species.
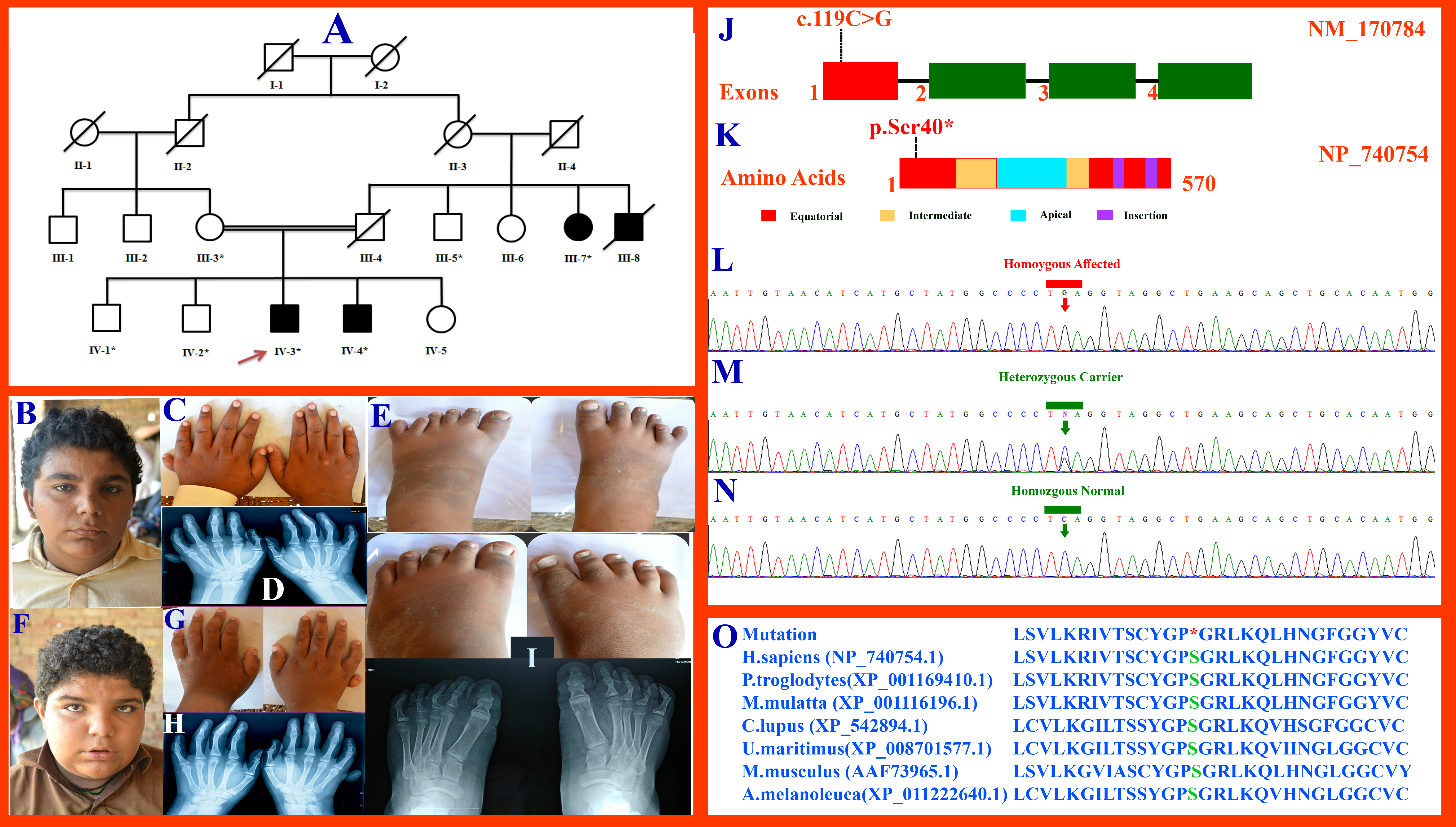
 Figure 2 of
Ullah, Mol Vis 2017; 23:482-494.
Figure 2 of
Ullah, Mol Vis 2017; 23:482-494.  Figure 2 of
Ullah, Mol Vis 2017; 23:482-494.
Figure 2 of
Ullah, Mol Vis 2017; 23:482-494. 