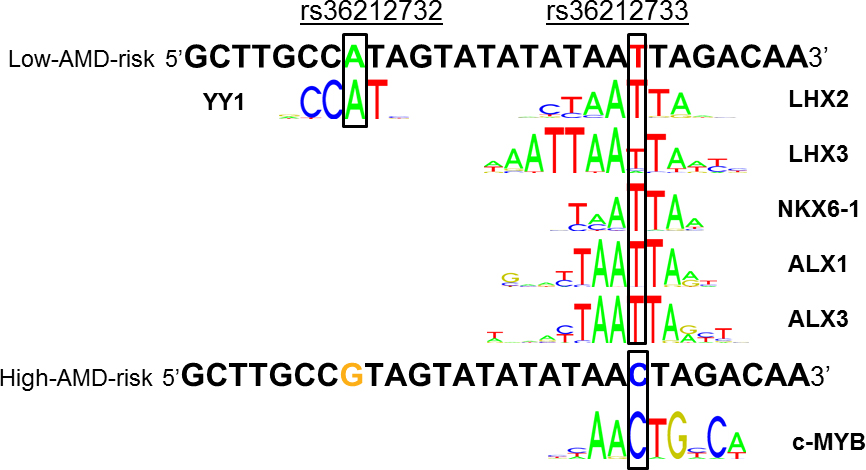
Figure 6. Changes in predicted transcription factor binding sites by SNPs associated with risk for AMD. The single nucleotide polymorphisms
(SNPs)
rs36212732 and
rs36212733 are 8–21 bp away from the telomeric boundary of an open chromatin region with the high DNase I sensitivity in RPE cells.
The low-AMD-risk haplotype has the base “A” at
rs36212732 and the base “T” at
rs36212733, while the high-AMD-risk allele has the bases “G” and “C” at the respective locations. In comparison with the low-AMD-risk
haplotype, the high-AMD-risk haplotype has a predicted reduction in the binding of the transcription factor YY-1, LHX2, LHX3,
NKX6–1, ALX1, and ALX3, and a predicted increase in the binding of the factor c-MYB, as predicted by the software HOMER, PROMO,
and RegulomeDB. The consensus YY-1, LHX2, LHX3, NKX6–1, ALX1, ALX3, and c-MYB binding sequences are from the JASPAR website.
 Figure 6 of
Liao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:318-333.
Figure 6 of
Liao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:318-333.  Figure 6 of
Liao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:318-333.
Figure 6 of
Liao, Mol Vis 2017; 23:318-333.