Figure 2. Intravitreal injection of RvD1 inhibited NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 expressions in rat retinas. A: Representative immunohistochemical images of the expression of Nod-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing (NLRP3),
caspase-associated recruitment domain (ASC), and caspase-1 in the retina. Immunohistochemical staining shows the location
of NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 expression in the ganglion cell layer (GCL) and the inner nuclear layer (INL). The number of
positive cells expressing NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 were remarkably increased in the group treated with streptozotocin (STZ)
compared with the control group. Intravitreal injection of resolvin D1 (RvD1) decreased the expression of NLRP3, ASC, and
caspase-1 compared with the STZ-treated group. The brown granules marked with arrows represent corresponding specific staining
(400X). Scale bar = 20 μm (n = 4). B: Quantification of the positive cells in the retinas. Three sections per eye were averaged. RvD1 decreased the number of
positive cells in the STZ-treated group compared with the RvD1 group. C: RvD1 treatment decreased the mRNA expression of NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 in the retinas of the STZ-treated rats. D: Representative western blot showing the protein expression of NLRP3 and ASC in the rat retinas. GAPDH was used as a loading
control. E: Column diagrams representing the ratio of the scanned immunoblots of NLRP3 and ASC to that of GAPDH. F: Representative western blot showing the protein expression of pro-caspase-1 and caspase-1 p20 in rat retinas. G: Column diagrams representing the ratio of the scanned immunoblots of pro-caspase-1 and caspase-1 p20 to that of GAPDH. Data
are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). *p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. n = 6 experiments.
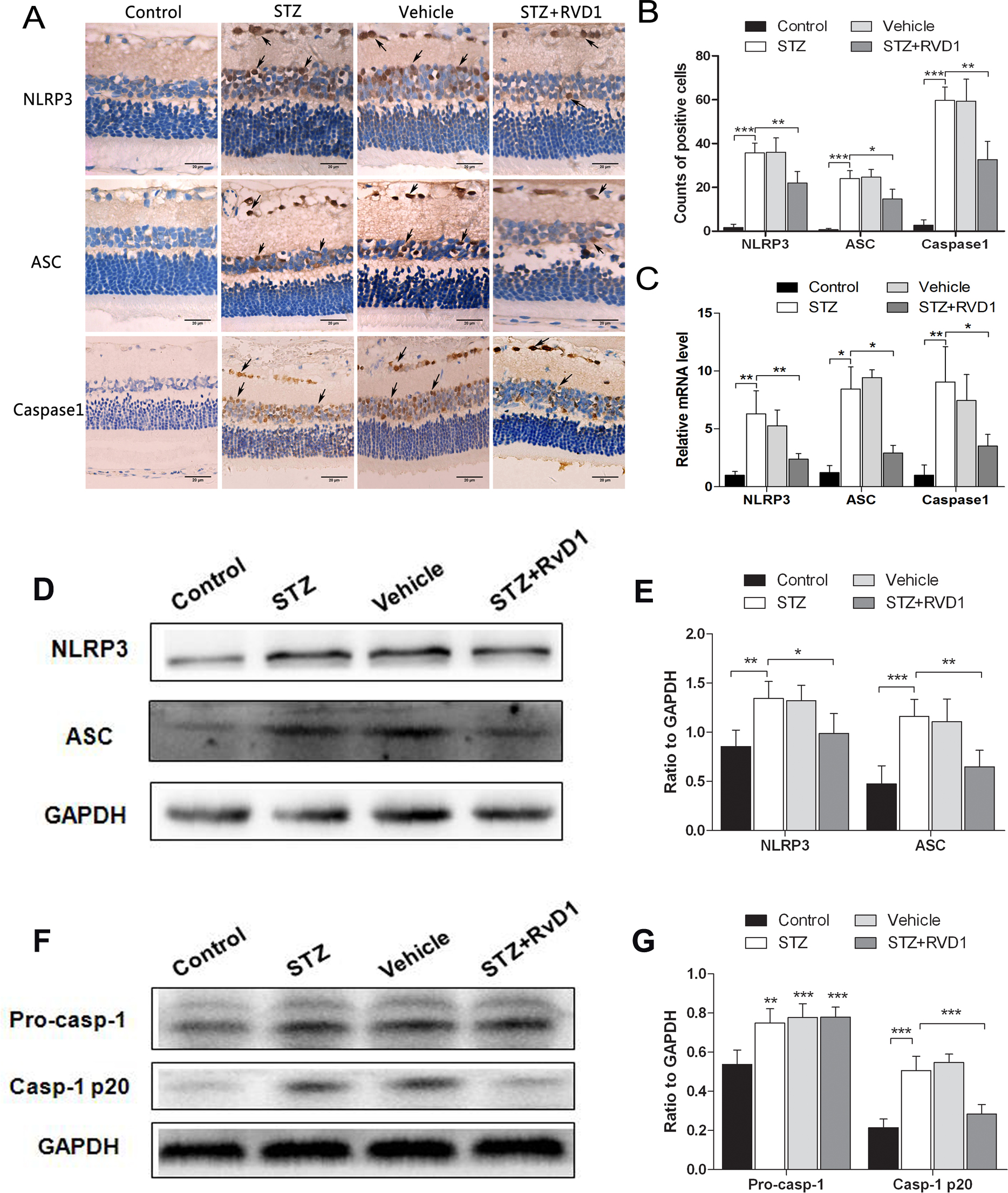
 Figure 2 of
Yin, Mol Vis 2017; 23:242-250.
Figure 2 of
Yin, Mol Vis 2017; 23:242-250.  Figure 2 of
Yin, Mol Vis 2017; 23:242-250.
Figure 2 of
Yin, Mol Vis 2017; 23:242-250. 