Figure 1. Chemical inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) blocks retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4)-induced endothelial inflammation.
A: TLR4 expression in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRECs) with and without treatment with 100 µg/ml RBP4
or the molar equivalent of bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 24 h. B: Interaction between TLR4 and adaptor molecule MyD88 in HRECs with and without RBP4 treatment for 30 min was analyzed with
immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblotting. Expression of TLR4 and MyD88 was analyzed by immunoblotting using total cell
lysates. C and D: Western blot and densitometry analyses of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) protein expression in HRECs treated
with RBP4 in the absence or presence of a 2-h preincubation of TLR4 chemical inhibitor Cli95. Bar graph data represent the
mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. E-I: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)-based quantification of soluble extracellular levels of (E) VCAM-1, (F) intracellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), (G) endothelial cell selectin (E-selectin), (H) monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1), and (I) interleukin 6 (IL-6) in HREC media. J: Representative phase-contrast images of leukocyte adhesion to HRECs after the indicated treatment. Data are representative
of four separate experiments. Magnification: 20×. K: The number of leukocytes adhering to HRECs was counted in four randomly selected visual fields (20× objective) for each
treatment group. **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001 versus BSA; #, p<0.05; ##, p<0.01; ###, p<0.001 versus RBP4; $$$, p<0.001 versus
lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test.
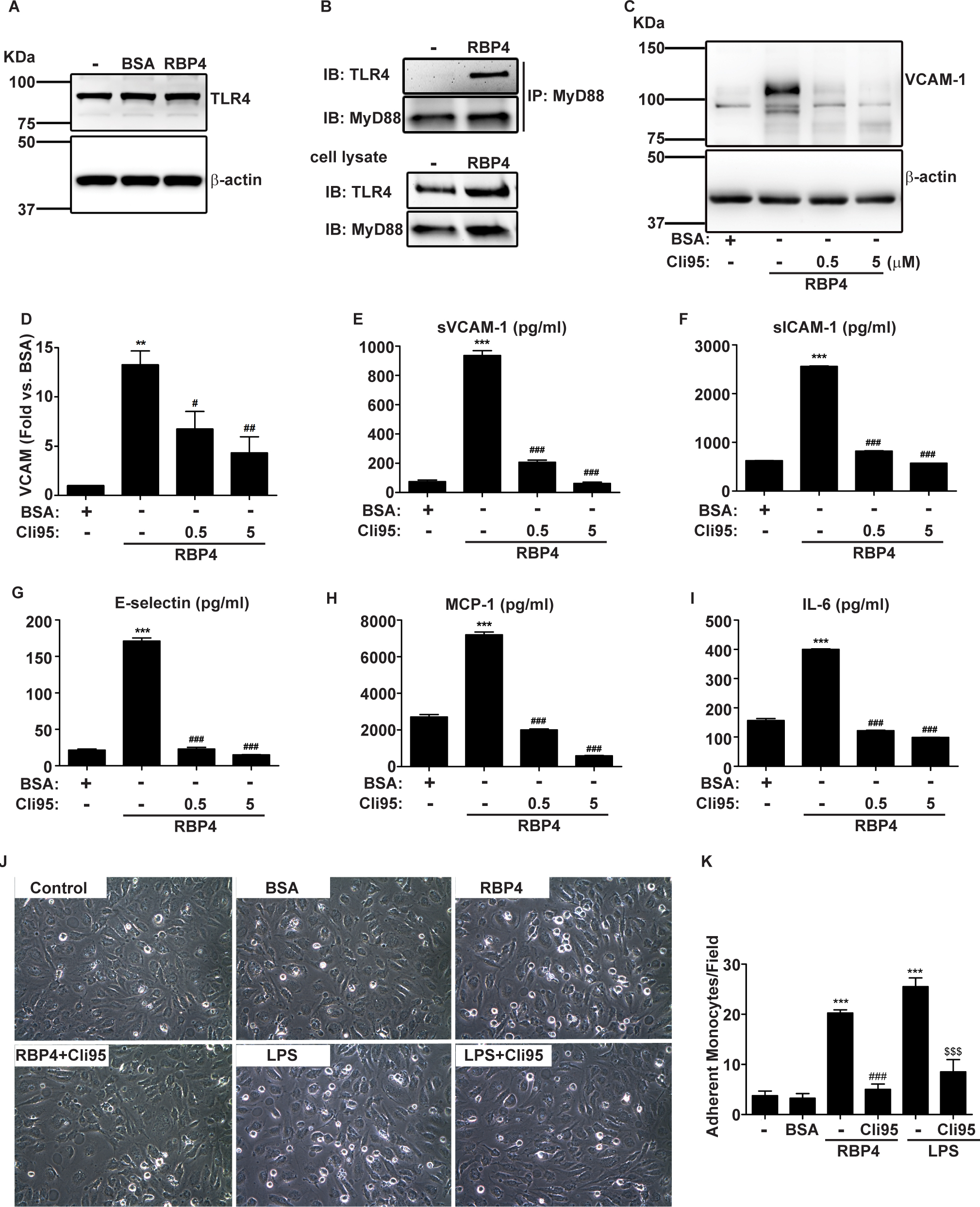
 Figure 1 of
Du, Mol Vis 2017; 23:185-197.
Figure 1 of
Du, Mol Vis 2017; 23:185-197.  Figure 1 of
Du, Mol Vis 2017; 23:185-197.
Figure 1 of
Du, Mol Vis 2017; 23:185-197. 